Near zero downtime maintenance with Red Hat Enterprise Linux for SAP Solutions
Avoiding preventative maintenance means welcoming reactive SAP ERP downtime
Is “near zero downtime” a myth for SAP ERP systems?
Minimizing downtime of SAP applications is a major concern for companies that use SAP enterprise resource planning (ERP). Technical downtime can lead to business downtime, which is unacceptable to end users.
Near zero downtime maintenance—also called nZDM—may be a familiar expression in the SAP field, but it is hard to achieve. We will look at an architecture and SAP downtime minimization that can help you navigate the risks of system conversion projects, database migrations, and other upgrade plans.
SAP host maintenance tends to be very inflexible. As a result, customers frequently put off version upgrades and operate SAP servers that are quite outdated. This helps SAP customers avoid unacceptable disruptions to the runtime environment, but it is not a viable downtime approach.
By running your SAP ecosystem on a Red Hat® platform, including Red Hat Enterprise Linux® for SAP Solutions, you can complete near zero downtime (nZDT) and activities on SAP hosts without unexpectedly ejecting end users out of a system or canceling background tasks. This architecture will walk you through some tools to keep your SAP systems updated while meeting downtime requirements.
Fear of business downtime and outages leads to inflexible maintenance windows
Companies need to comply with many recommendations from SAP and the operating system (OS) vendor, which makes it important to keep the hosts and workloads up to date.
Unfortunately, IT teams are often unable to update their SAP systems because the business cannot afford to take them offline—basically, technical downtime leads to business downtime. As a result, planned downtime and maintenance windows for important tasks like data migration, project cutover, and other critical work are scarce and very short. As a result, it is challenging for the teams responsible for SAP Basis, the operating system, and the infrastructure to finish their interventions properly and on time.
Maintenance windows often take place outside business hours, at least for production systems. This timeline forces IT teams to spend nights or weekends scrambling to get the SAP systems back up and running, with the new updates applied, before the end of the maintenance window.
For these reasons, SAP customers commonly put off version upgrades of the OS until their current ones become unsupported.
Achieving nZDM and downtime-optimized conversion
So, how do you plan for upgrades (for instance, a SAP S/4HANA® conversion) while navigating limited downtime options and notification requirements? In this detail, we describe a solution to this problem using a combination of products, including Red Hat Enterprise Linux High Availability Add-On, Red Hat Satellite, and Red Hat Ansible® Automation Platform, to detect issues before they arise and automatically deploy remediation to your environment, all without requiring immediate and unexpected system restarts or lengthy maintenance windows.
Of course, there are unavoidable updates that require system restarts, such as kernel patches or system updates. However, applying remediations now and scheduling reboots for a future date, during a normal maintenance window, gives you control over these maintenance windows with less risk of running out of time before the work is complete.
What’s in a nDZM architecture?
In this section, we will dig deeper into an architecture for downtime minimization and downtime optimization, including a generic look at what a NZDT solution would look like. We’ll review components that make up this sort of solution and how it can benefit someone looking to maximize available resources.
Benefits of a near zero downtime architecture
The main business objectives of a nZDT solution are to manage and maintain all of your SAP ERP hosts, keeping them up to date, compliant, and consistent across your hybrid cloud estate, all while avoiding normal disruptions (including disruptions caused by planned maintenance windows). The goal of technical downtime optimization is to reduce the impact of system maintenance, whether scheduled or unscheduled, to as close to zero as possible.
Below are some key definitions and components of a generic nZDM solution.
What is a hybrid cloud solution?
A hybrid cloud is a solution in which applications run in a combination of different environments, including physically on-premise and virtually in the cloud. The type of cloud environment is not locked in, so it can be public, private, or a combination of both.
For example, we often see customers run a development or testing environment in a public cloud, while the quality engineering environment is in a private cloud, and finally, the production environment is hosted on-premise. A hybrid cloud solution can span the entire estate, allowing for versatility in application management and simplifying the complexity of the environment.
What is high availability?
The term “high availability” denotes a certain threshold of uptime and increased reliability in operations being performed by a system. This is typically delivered by eliminating single points of failure in an environment so that an application, database, or another type of workload can run without interruption.
What is system management?
In this context, system management is a centralized platform that handles day-to-day IT administration, from content and patch management and deployments to subscription utilization and governance.
Here are a few of the most common—and critically important—system management tasks.
- Content management. For systems to remain up to date, a software update manager and similar tools handle regular system updates.
- Patch management. Beyond just keeping systems up to date, administering patching against security vulnerabilities, software bugs, and similar threats ensure that systems are continuously secure.
- Provision management. System provision management allows systems to be deployed at specific baseline states, which creates consistency across the environment.
- Subscription management. Whether managing subscriptions for your own organization, or for the customers you are servicing, subscription management can be a major roadblock in a project. Making sure the governance of subscriptions usage is simple, comprehensive, and reliable is key to success.
What is automation?
Automation is the practice of eliminating reliance on human and manual interventions to complete a set of objectives. With automation, teams increase efficiency by removing sometimes tedious or menial tasks that are required for day-to-day operations and maintenance, so they can reallocate technical administrators, operators, and other skilled staff to the workloads that matter for innovating and advancing the business.
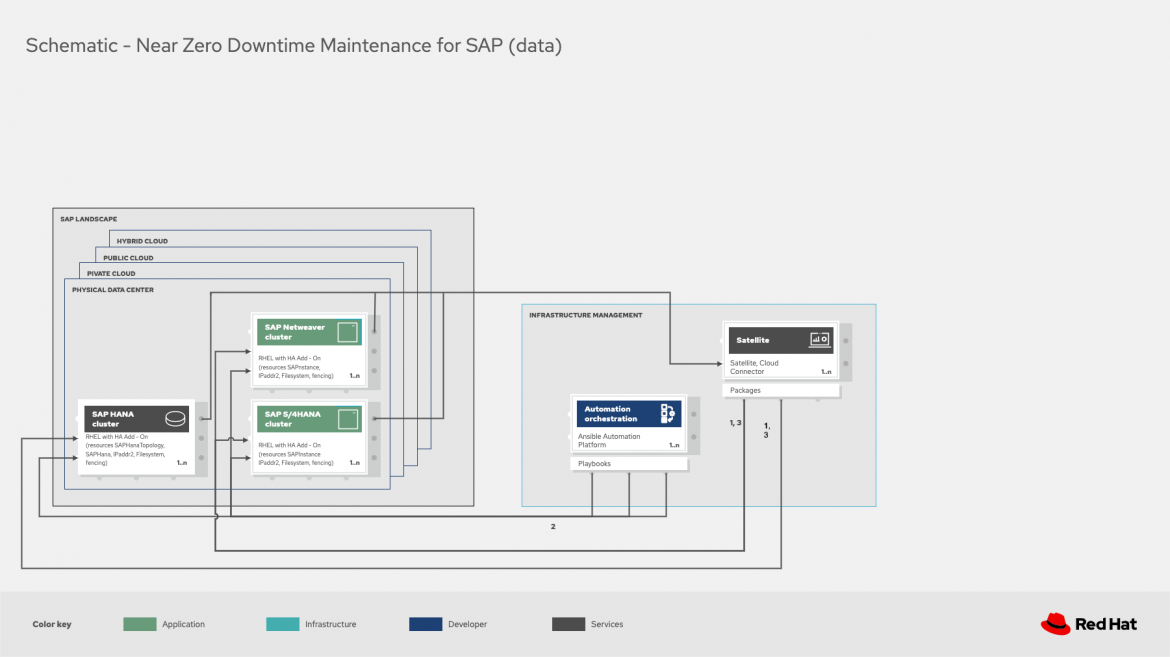
Red Hat portfolio architecture: Near zero downtime maintenance with Red Hat Enterprise Linux for SAP Solutions
The core of nZDT platforms for SAP is the Red Hat Enterprise Linux for SAP Solutions subscription, which covers the operating system, Red Hat Enterprise Linux High Availability Add-On, and Red Hat Satellite for system management. With these three together, the operating system will uptime with the High Availability Add-On, while Red Hat Satellite helps maintain and manage normal daily operations of the entire Red Hat Enterprise Linux estate, regardless of location. So, whether on-premise or in the cloud, you can manage your environment at scale. In addition, this subscription provides Red Hat Insights, which offers detection and remediation planning for any potential issues before they occur.
The remaining piece of the puzzle that orchestrates the entire update process is Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform. It is integrated with Red Hat Enterprise Linux for SAP Solutions to provide a complete, robust, and easily managed platform for SAP workloads like SAP HANA databases.
Let’s review how these different Red Hat technologies work together to create a simple platform for even the most demanding SAP workloads.
What is Red Hat Enterprise Linux?
Red Hat Enterprise Linux is a leading enterprise operating system that is certified on hundreds of clouds and with thousands of vendors. Red Hat Enterprise Linux provides a consistent foundation across environments and the tools needed to deliver services and workloads faster for any application. Red Hat Enterprise Linux reduces deployment friction and costs while speeding time to value for critical workloads, helping development and operations teams innovate together in any environment.
What is an open hybrid cloud?
Open hybrid cloud is Red Hat's recommended strategy for designing, developing, and operating a hybrid mix of applications, delivering a truly flexible cloud experience with the speed, stability, and scale required for digital business transformation. Red Hat’s open hybrid cloud strategy is built on the technological foundation of Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Red Hat OpenShift®, and Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform.
This strategy gives developers a common application environment to develop, orchestrate, and run their applications. It also gives system administrators and operations teams a common operating environment to manage a diverse infrastructure. With this consistency across environments, you can deliver automated IT infrastructure.
What is the Red Hat Enterprise Linux High Availability Add-On?
The Red Hat Enterprise Linux High Availability Add-On makes creating clusters possible on both the database and the application side. It features lock management, cluster management and fencing mechanisms (STONITH and SBD). It also includes specific resources for the ABAP SAP programming language, such as ABAP Central Service (ASCS) and Evaluation Receipt Service (ERS) instances. These resources work for all SAP-supported workloads, including SAP HANA databases.
What is Red Hat Satellite?
Red Hat Satellite is an infrastructure management product specifically designed to keep Red Hat Enterprise Linux and other Red Hat infrastructure running efficiently, with security, and in compliance with various standards. It can manage your entire infrastructure—not just Red Hat Enterprise Linux systems—from a single console.
In this solution, Red Hat Satellite manages the life cycle of the SAP hosts and makes sure there is consistency across the SAP HANA database, with the same content, patches, and security fixes on all the servers.
Red Hat Satellite gives users the power to manage systems across several important dimensions.
- Content management: Satellite uses a curated content repository that is distributed consistently to all hosts. It brings curated content as close as possible to the systems being managed.
- Patch management: Satellite reports on hosts that need updates, fixes, or enhancements and applies them automatically when approved.
- Provision management: Satellite provisions to bare metal, virtual, private, public, and hybrid clouds. It uses Ansible Roles to automate post-provisioning steps.
- Subscription management: Satellite centrally manages the subscriptions of all SAP hosts and keeps track of their subscription consumption, maintaining accurate inventory and utilization information.
What is Red Hat Insights?
Red Hat Insights is a proactive operational efficiency and security risk management solution. With advanced analytics, Red Hat Insights identifies and prioritizes risks to your operations, security, and business. Insights also helps users monitor for adherence to policies and understand configuration changes over time.
With Red Hat Insights, you gain all the key benefits of avoiding unplanned downtime and better managing security risks while resolving potential problems quickly by understanding where to focus attention, ultimately easing maintenance administration with a single tool.
What is Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform?
Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform orchestrates the solution using Ansible Playbooks that automate the whole process of SAP database maintenance (OS kernel upgrades, OS parameter changes, software update manager notifications, security fixes, SAP Notes and HANA revision updates, SAP HANA parameter changes, SAP kernel upgrades, and more).
It is also the central point from which the entire SAP HANA database estate can be managed following an Infrastructure-as-Code approach, with inventories for different types of servers, departments in the company and adding a granular layer of security with role-based access control (RBAC).
What is an Ansible Playbook?
An Ansible Playbook is a blueprint of automation tasks—which are complex IT actions executed with limited or no human involvement. Ansible Playbooks executed on a set, group, or classification of hosts, which together make up an Ansible inventory.
They are essentially frameworks of prewritten code that developers can use ad hoc or as starting templates to automate IT infrastructure. Ansible Playbooks help IT staff program applications, services, server nodes, and other devices without the manual overhead of creating everything from scratch. Playbooks, including the conditions, variables, and tasks within them, can be saved, shared, or reused indefinitely.
This solution uses the high availability capabilities of SAP HANA system replication, but since this does not provide for automatic fail-over of resources, a pacemaker cluster is implemented, creating a replica of the database. As a result, application servers remain connected to a running instance of the SAP HANA database and can work continuously, without interruptions.
Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform orchestrates the entire process, triggering the fail-over of the cluster resources to the node that is not being upgraded and launching the update tasks in the target servers.
Red Hat Satellite manages patching and updating for purely OS-related interventions like an OS version upgrade, security fixes, or application errata. Ansible Automation Platform triggers and carries out the execution across the specified environment.
Ansible Automation Platform augments user control by employing playbooks for SAP HANA upgrades, changes in the SAP HANA database or OS parameter, and SAP kernel updates.
Here is how the solution works, using an example of Netweaver or SAP S/4HANA with an SAP HANA scale-up implementation using SAP HANA system replication. This process is considered maintenance on the SAP HANA hosts.
Steps of the process:
- The virtual IP resource of the cluster used to connect the application to the SAP HANA database initially points to the primary SAP HANA node. Ansible Automation Platform triggers the intervention on the secondary SAP HANA node. The intervention is triggered from Satellite or the Ansible Playbook, depending on whether the task is a system process managed by Red Hat Satellite.
- Once the intervention is finished on the secondary SAP HANA node, Ansible Automation Platform triggers the fail-over of the virtual IP resource of the cluster so that it will point to the node that has been maintained. It also promotes the SAP HANA database in this node to primary and reverts the direction of SAP HANA system replication. Using the connectivity suspend feature introduced in SAP Netweaver 7.40 SP 5 (see this SAP Note), users will not perceive any disconnection while the cluster resources are failed over and promoted or demoted.
- Ansible Automation Platform triggers the maintenance on the former primary SAP HANA node. After it is finished, the administrator can either revert to the initial situation, failing back the resources, or maintain the current one.
Red Hat’s approach to helping you avoid business downtime
To maintain a company's throughput and high productivity, solutions that eliminate disruptions and promote reactive downtime are crucial. By using Red Hat’s platform to achieve near zero downtime maintenance, you can remain up to date, compliant, and consistent across your hybrid cloud estate, all while avoiding the disruptions normally faced with SAP solution upgrades and changes.
To learn more, or to contribute to our growing list of architectures, visit Red Hat’s portfolio architecture.