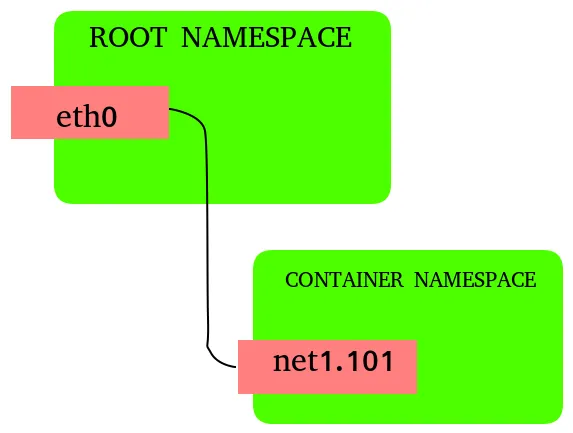
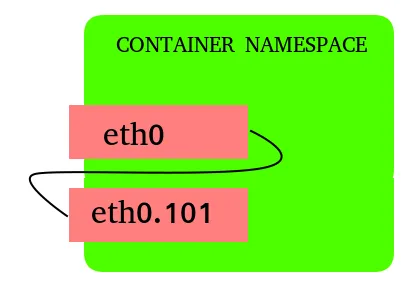
Until recently, the existing vlan/macvlan/ipvlan CNI plugins only allowed users to create a VLAN subinterface based on a master interface in the host network namespace, and place the VLAN subinterface inside the container namespace.
Vlan based on node namespaced master
This approach had several drawbacks, the main being issues connected to configuration:
- A preconfigured master interface had to be present on the nodes.
- The vlan/macvlan/ipvlan configuration required knowledge about the node network configuration.
- Multiple network-attachment-definitions needed to be configured to use with different master/vlan combinations. Effectively a single network-attachment-definition could only be used on only one pod.
- The network-attachment-definitions had to be bound to nodes, since the available masters on different nodes could differ.
- The user had to keep track of which master/vlan combinations were already in use.
A recent feature coming in OpenShift 4.13 (Developer Preview) allows the vlan/macvlan/ipvlan interfaces to be configured using container namespace master interfaces.
Vlan based on container namespaced master.
This allows to create the master interfaces as part of the pod network configuration in a separate network-attachment-definition, and base the vlan/macvlan/ipvlan on this interface without requiring the knowledge of the network configuration of the node.
Installing
The feature will be available in OpenShift 4.13 as Developer Preview. No further installation is required.
Configuring a vlan/macvlan/ipvlan with container namespace master
To request the use of a container namespace master interface a new parameter “linkInContainer” has been added to the vlan/macvlan/ipvlan plugin configuration:
{
"name": "mynet",
"cniVersion": "0.4.0",
"type": "vlan",
"master": "eth0",
"mtu": 1500,
"vlanId": 73,
"linkInContainer": true
}
A sample use case for the use of the new feature is to create VLANs based on SR-IOV Virtual Functions. For this a SR-IOV network must be created, followed by the network-attachment definitions for the VLAN interface:
---
apiVersion: sriovnetwork.openshift.io/v1
kind: SriovNetwork
metadata:
name: sriov-network
namespace: openshift-sriov-network-operator
spec:
networkNamespace: mynamespace
resourceName: sriovnic
spoofChk: "off"
trust: "on"
---
apiVersion: sriovnetwork.openshift.io/v1
kind: SriovNetworkNodePolicy
metadata:
name: sriovnic
namespace: openshift-sriov-network-operator
spec:
deviceType: netdevice
isRdma: false
needVhostNet: true
nicSelector:
pfNames:
- ens3f0#0-4
numVfs: 10
priority: 99
resourceName: sriovnic
Followed by a VLAN network-attachment definition:
apiVersion: k8s.cni.cncf.io/v1
kind: NetworkAttachmentDefinition
metadata:
name: vlan-73
namespace: mynamespace
spec:
config: '{
"cniVersion": "0.4.0",
"name": "vlan-73",
"plugins": [
{
"type": "vlan",
"master": "ext0", ⓿
"mtu": 1500,
"vlanId": 73,
"linkInContainer": true, ❶
"ipam": {...}
}
]
}'
Note ⓿: the vlan configuration needs to specify the master name. This can be configured in the pod networks annotation, as shown below.
Note ❶: the linkInContainer parameter must be specified
The pod definition using the above specified networks must use the following networks annotation:
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
annotations:
k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/networks: '[
{
"name": "sriov-network",
"namespace": "mmirecki",
"interface": "ext0" ❷
},
{
"name": "vlan-73",
"namespace": "mmirecki",
"interface": "ext0.73"
}
]'
Note ❷: The name to be used as the master for the vlan interface.
Use case example
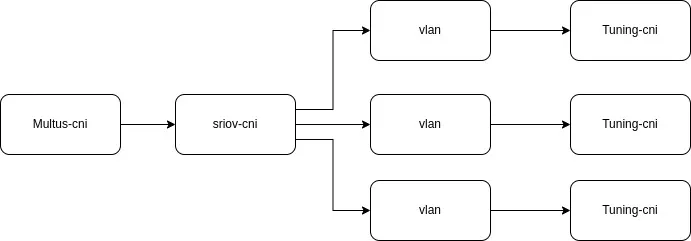
A example use case for this feature is the use of the vlan/macvlan/ipvlan based on SR-IOV virtual functions.
Multiple VLANs can be used with a single virtual function as the master interface. To allow additional configuration the tuning plugin can be used to further tune the created VLAN interfaces. The entire process can be performed in an automated manner, with no knowledge about the node interfaces other than that required to configure the SRIOV plugin.
Status
The TAP device feature will be available in OpenShift 4.13 as Developer Preview.
The use cases for the feature and available options are based on limited customer feedback. Additional feedback on possible use cases and missing functionality are welcome. Please contact your Red Hat account manager for further details.
About the author
Browse by channel
Automation
The latest on IT automation for tech, teams, and environments
Artificial intelligence
Updates on the platforms that free customers to run AI workloads anywhere
Open hybrid cloud
Explore how we build a more flexible future with hybrid cloud
Security
The latest on how we reduce risks across environments and technologies
Edge computing
Updates on the platforms that simplify operations at the edge
Infrastructure
The latest on the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform
Applications
Inside our solutions to the toughest application challenges
Original shows
Entertaining stories from the makers and leaders in enterprise tech
Products
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux
- Red Hat OpenShift
- Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform
- Cloud services
- See all products
Tools
- Training and certification
- My account
- Customer support
- Developer resources
- Find a partner
- Red Hat Ecosystem Catalog
- Red Hat value calculator
- Documentation
Try, buy, & sell
Communicate
About Red Hat
We’re the world’s leading provider of enterprise open source solutions—including Linux, cloud, container, and Kubernetes. We deliver hardened solutions that make it easier for enterprises to work across platforms and environments, from the core datacenter to the network edge.
Select a language
Red Hat legal and privacy links
- About Red Hat
- Jobs
- Events
- Locations
- Contact Red Hat
- Red Hat Blog
- Diversity, equity, and inclusion
- Cool Stuff Store
- Red Hat Summit