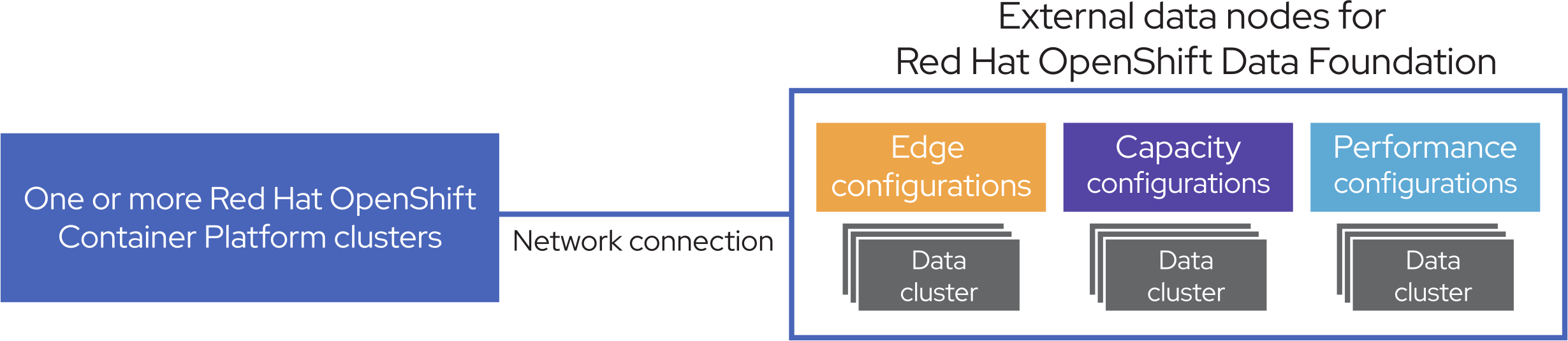
Data node configurations for Red Hat OpenShift
Workload-specific data services infrastructure
Organizations need data services that are optimized for specific workloads, particularly as digital transformation efforts escalate and new cloud-based development and deployment methodologies take hold. With the rapid increase in data volumes and increasingly complex data pipelines, monolithic cloud storage is often inadequate. Edge applications, analytics workloads, and databases all have distinct requirements for access, capacity, and performance. Few organizations have time to evaluate and test various combinations of hardware and software to determine their suitability for diverse workloads.
To address these challenges, Red Hat and Intel are testing persistent software-defined storage solutions in cloud-native Kubernetes environments. Together, the companies focus on workload-optimized data services solutions based on sophisticated software-defined storage and innovative hardware technologies. This collaboration has resulted in tested data node configurations for Red Hat® OpenShift® targeted at edge, capacity, and performance workloads.
Red Hat OpenShift and Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation, combined with recommended Intel® technology-based data node configurations, offer distinct advantages that include:
- Scalable data services for Red Hat OpenShift applications.
- Tested configurations that gain efficiency in less time.
- A vastly simplified evaluation process for data services infrastructure.
- Configurations optimized for edge, capacity, and performance workloads.
Highlights
Deploy workload-specific data node configurations for your most demanding applications, no matter where they run.
Scale Red Hat OpenShift apps with workload-optimized data nodes for edge, capacity, or performance-intensive workloads.
Separate compute and storage for flexibility, scalability, and sharing using Red Hat OpenShift Platform Plus and Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation Advanced.
Rely on innovative and proven Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors and Intel® Optane™ Solid State Drives (SSDs) and Intel® Optane™ Persistent Memory for optimized storage performance.
Data node configurations for Red Hat OpenShift
Workload-optimized data node configurations for OpenShift Data Foundation (Figure 1) are based on Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors, Intel® Optane™ technology, and Intel® Ethernet technology, the range of configuration choices lets you quickly and easily procure and deploy the appropriate data nodes for specific workloads—from edge computing to high capacity for data analytics to high performance for latency-sensitive database applications.
Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation
Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation is persistent software-defined storage integrated with and optimized for Red Hat OpenShift. Based on leading industry technologies that provide petabyte-scale persistent cloud storage, a Kubernetes storage operator, and multicloud object gateway technology, OpenShift Data Foundation runs anywhere that Red Hat OpenShift does—on-premise or in cloud environments. OpenShift Data Foundation is included as a part of a complete offering called OpenShift Platform Plus,1 letting organizations rapidly and conveniently deploy OpenShift clusters while provisioning and deprovisioning dynamic, stateful, and highly available container-native storage on demand. OpenShift Platform Plus takes the guesswork out of deploying Red Hat OpenShift clusters by including:
- Multicluster management.
- Cluster security.
- Global registry.
- Cluster data management services.
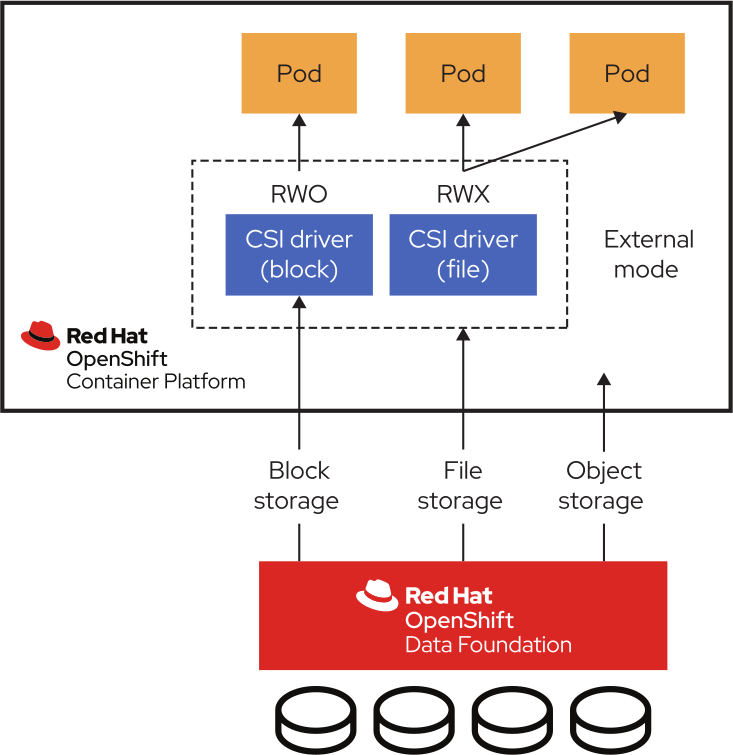
As container-based application demands escalate, organizations are realizing the benefits of scaling compute and storage independently. Intel data node configurations support this logical separation by combining OpenShift Platform Plus with OpenShift Data Foundation Advanced edition. With support for an external-mode deployment, OpenShift Data Foundation Advanced edition allows one or more OpenShift Container Platform clusters to access an independently optimized and managed storage cluster (Figure 2). It also allows organizations to consume storage services both for workloads within Red Hat OpenShift clusters, as well as off-cluster workloads. With enhanced volume-level security, key management system support, and additional cluster resiliency options, the powerful combination of OpenShift Platform Plus with OpenShift Data Foundation Advanced edition helps solution architects address their specific workload needs while preserving a common, consistent storage services interface.
OpenShift Data Foundation Advanced external storage clusters are massively scalable, support mixed media types, and expand tuning options for diverse workloads. Decoupled storage clusters can be scaled as needed. Multiple Red Hat OpenShift clusters can consume storage from an external cluster, easing data sharing between Red Hat OpenShift clusters and applications. This flexibility also allows individual data nodes to be customized and optimized for specific workloads using the most appropriate Intel technology.
Intel Xeon Scalable processors
Intel Xeon Scalable processors benefit from decades of innovation in support of our customers' most demanding workloads. With a balanced architecture, these processors are optimized for many workload types and performance levels including cloud, enterprise, high-performance computing (HPC), network, security, and Internet of Things (IoT). With 8-40 powerful cores and a wide range of frequency, feature, and power levels, Intel Xeon Gold processors are ideal for OpenShift Data Foundation data nodes.
Intel Optane Solid State Drives (SSD)
Intel Solid State Drive (SSD) technology is critical for optimizing OpenShift Data Foundation performance for different workloads. Intel Optane SSDs are used to house the Ceph® metadata cache for most data node configurations. This approach takes the write pressure off of the Ceph storage media, creating a solution that is optimized for both input/output (I/O) operations per second (IOPS) and total cost. Featuring a memory-like capability inside an SSD form factor, Intel Optane SSDs are fundamentally different from other SSDs. This design gives them lower latency, higher IOPS performance, and greater endurance. For example, Intel Optane SSDs support an industry-leading 100 drive writes per day (DWPD).2
The right data node configuration for your workload
Unlike many cloud storage solutions, OpenShift Data Foundation supports file, block, and object storage access methods in a single solution, allowing it to support a wide range of Red Hat OpenShift applications. For certain workloads, storage performance can be optimized by placing the Ceph metadata cache on high-speed media (for example, Optane). The sections that follow describe specific data node configurations for OpenShift Data Foundation. Red Hat and its partners offer both base and plus configurations for each data node category, allowing for precise sizing and scalability.
Data nodes optimized for edge infrastructure
Investments in edge computing are growing at double-digit rates, and will continue this trend through 2025.3 The ability to manage large volumes of data being generated and collected at the edge—or distributed to the edge— is an ever growing consideration as organizations extend and innovate closer to the source of data. Edge applications are wide-ranging and include software-defined networking (SDN) and network functions virtualization, media streaming, security and surveillance, analytics storage tiering, automated data pipelines, clinical applications in healthcare settings, customer engagement in smart retail, insurance claim generation, and defect detection and quality control in manufacturing settings. These applications have varying requirements, but they all need agile infrastructure that provides cost-effective storage.
Edge servers require smaller footprints and lower power consumption, but still need to process demanding streaming, analytics, and database workloads with low latency and high throughput. Table 1 describes data node configurations for provider and enterprise edge infrastructure using Intel Xeon Scalable processors, SSDs, and networking components.
- Edge base configuration. This data node configuration allows for lower power consumption and balanced processing for environments where there is less demand for throughput.
- Edge plus configuration. This data node configuration includes dual processors for heavier edge computing requirements and adds an Intel Optane SSD P5800X as a Ceph metadata cache for higher throughput demands.
Table 1. Data node configurations optimized for edge computing
| Base configuration (10TB) | Plus configuration (20TB) | |
| Platform | Single 2U node | |
| CPU | 2x Intel Xeon Gold 5318Y processor (24 cores) | 2x Intel Xeon Gold 5318Y processor (24 cores) |
| Memory | 96GB | 192GB |
| Data network | 2x Intel Ethernet Network Adapter 810-CQDA2 (10GbE) | |
| Management network | 1x Intel Ethernet Connection X710-DA2 (10GbE) | |
| Metadata cache | 1x Intel Optane SSD P5800 (400GB) | 1x Intel Optane SSD P5800X (800GB) |
| Storage media | 6x SSD (1.92TB, 2.5-inch SATA, TLC) | 6x SSD (3.84TB, 2.5-inch SATA, TLC) |
Data nodes optimized for capacity
Cost-effective, high-capacity storage is essential for big data and analytics workloads. Data lakes act as a centralized repository for both structured and unstructured data, letting you run different types of analytics workloads on demand. High-capacity multipetabyte storage lets organizations use big data processing, real-time analytics, and machine learning to guide better decisions. Fraud detection, business intelligence, and reporting for Presto and PostgreSQL are other application areas that require sifting through massive amounts of information for recognizable patterns.
Capacity-oriented servers need to meet the demands of big data and analytics workloads. Beyond simple storage capacity, servers must be sized to actually process tens of terabytes of storage. Table 2 describes data node configurations optimized for capacity.
- Capacity base configuration. This capacity-optimized data node allows for 30TB of data storage along with the networking and processing capability to handle data sets of that size.
- Capacity plus configuration. This data node expands storage to 60TB, doubles the number of processors, doubles the amount of system memory, and provides a Ceph metadata cache built from two Intel Optane SSDs.
Table 2. Capacity-optimized data node configurations
| Base configuration (30TB) | Plus configuration (60TB) | |
| Platform | Single 2U node | |
| CPU | 2x Intel Xeon Gold 5320 processor (26 cores) | 2x Intel Xeon Gold 6330 processor (24 cores) |
| Memory | 96GB | 192GB |
| Data network | 2x Intel Ethernet Network Adapter 810-CQDA2 (25 GbE) | |
| Management network | 1x Intel Ethernet Connection X710-DA2 (10GbE) | |
| Metadata cache | 1x Intel Optane SSD P5800X (800GB) | 2x Intel Optane SSD P5800X (800GB) |
| Storage media | 8x SSD (3.84TB, 2.5-inch SATA, TLC) | 16x SSD (3.84TB, 2.5-inch SATA, TLC) or 8x SSD (7.68TB, 2.5-inch SATA, TLC) |
Data nodes optimized for I/O performance
Applications like streaming analytics, massively parallel data ingest, and cloud-native application development require high-performance data storage in addition to capacity. Database applications like PostgreSQL and Trino need low-latency data storage in order to provide reliable application performance. These performance and latency-sensitive applications demand data node configurations with fast networking and metadata acceleration from Intel Optane SSDs.
Table 3 depicts data node configurations optimized for performance.
- Performance base configuration. This data node configuration features two 20-core Intel Xeon Gold 6242R processors, 384GB of memory, and two Intel Optane SSD SD P5800X for the Ceph metadata cache.
- Performance plus configuration. This data node configuration expands those capabilities to deliver more optimized performance with more processor cores, more memory, higher bandwidth networking, and additional high-performance storage capacity.
Table 3. I/O performance-optimized data node configurations
| Base configuration (15TB) | Plus configuration (30TB) | |
| Platform | Single 2U node | |
| CPU | 2x Intel Xeon Gold 6338 processor (32 cores) | 2x Intel Xeon Gold 6338 processor (32 cores) |
| Memory | 192GB | 384GB |
| Data network | 2x Intel Ethernet Network Adapter E810-CQDA2 (50GbE) | 2x Intel Ethernet Network Adapter E810-CQDA2 (100GbE) |
| Management network | 1x Intel Ethernet Connection X710-DA2 (10GbE) | |
| Metadata cache | 2x Intel Optane SSD P5800X (800GB) | 2x Intel Optane SSD P5800X (1.6TB) |
| Storage media | 4x SSD (3.84TB, 2.5-inch U.2 NVMe, TLC) | 8x SSD (3.84TB, 2.5-inch U.2 NVMe, TLC) |
Conclusion
Together, Red Hat and Intel are developing combined software and hardware solutions that target the growing need for container data services in artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML), analytics, databases, and edge computing workloads. The unique combination of Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation external mode and optimized data node configurations from Intel dramatically simplifies the procurement and deployment life cycle for software-defined data storage infrastructure. With configurations that are tested and verified for capacity and bandwidth, organizations can focus on their applications, scaling as needed to meet application demand.
To get started with workload-optimized data node configurations for Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation, take these specifications to your hardware vendor of choice.
OpenShift Platform Plus includes OpenShift Data Foundation Essentials edition. Intel data nodes for Red Hat Openshift require OpenShift Data Foundation Advanced edition.
Intel® product brief: Intel® Optane™ SSD P5800X Series
Enterprise and service provider spending on hardware, software, and services for edge solutions is forecast to sustain growth through 2025 when spending will reach nearly $274 billion, according to IDC Press Release, "New IDC Spending Guide Forecasts Double-Digit Growth for Investments in Edge Computing," January 2022.