Last year Ansible Automation Platform (AAP) 2 introduced major changes around the mechanics on how automation is run. The main focus was to enhance the foundational pieces of the platform while providing flexibility and simplicity for automators to automate at enterprise scale. One of those foundational pieces introduced was automation mesh.
Automation mesh provides a simple, flexible and reliable way to scale automation of large inventories across diverse network topologies, platforms and teams. It was important to evolve how the platform was developed, managed, operated to meet business demands and needs, for the large majority of customers.
Pre 2.3 Automation Mesh in OCP
Prior to AAP 2.3, the automation mesh was mostly a VM deployment base option and feature. I’ve tried to highlight the main differences between platform choices in this diagram:
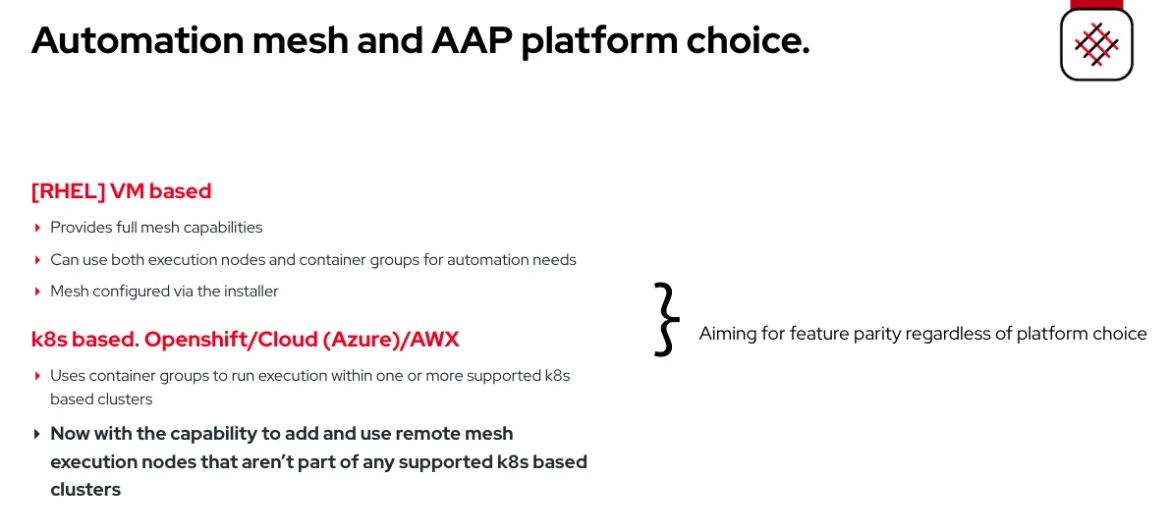
We are now starting to level up the feature parity, and this brings remote mesh execution nodes to non-VM supported deployments. Before we look more at the new feature, let’s look at the options that were available before:
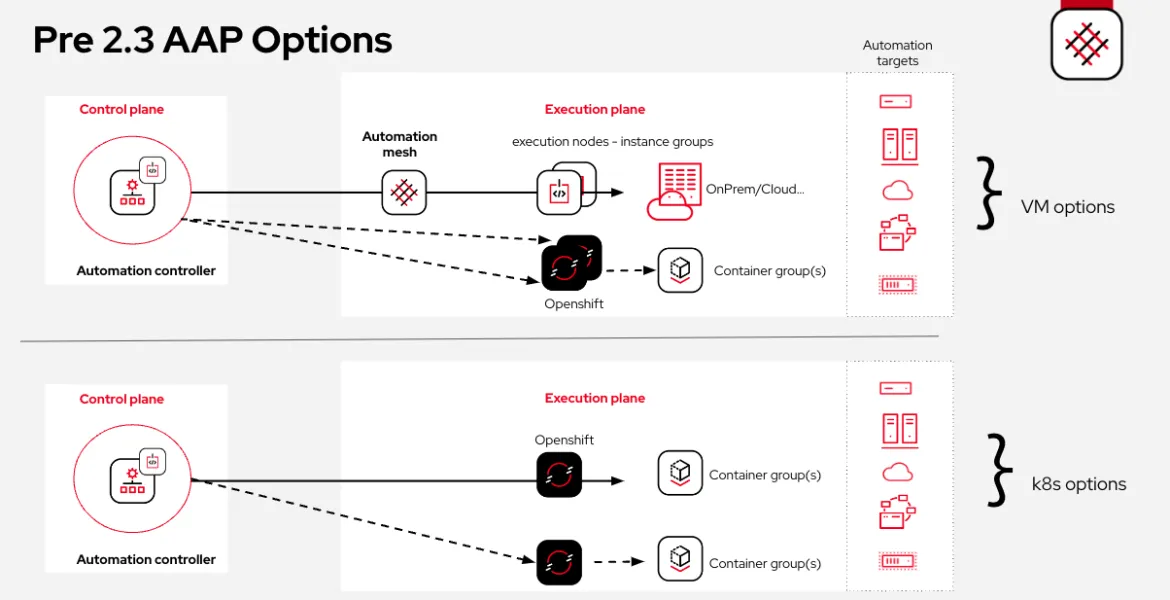
For VM based deployments, the automation mesh introduced horizontal scaling, the ability to scale your automation needs out, whether locally or globally. We did this by installing execution and hop nodes where we needed them, to allow us to wrap new style automation around the existing instance group functionality.
For non-VM based deployments, such as those running on Red Hat OpenShift, you could only target automation using container groups, which made use of the Kubernetes API to create dynamic containers for runtime automation.
This was fine if that was all you needed, were all in on the kubernetes cloud native approach, but left a gap if you needed a more traditional, hybrid configuration, so allow you to run workloads in different locations or environments.
2.3 Automation Mesh in Red Hat OpenShift
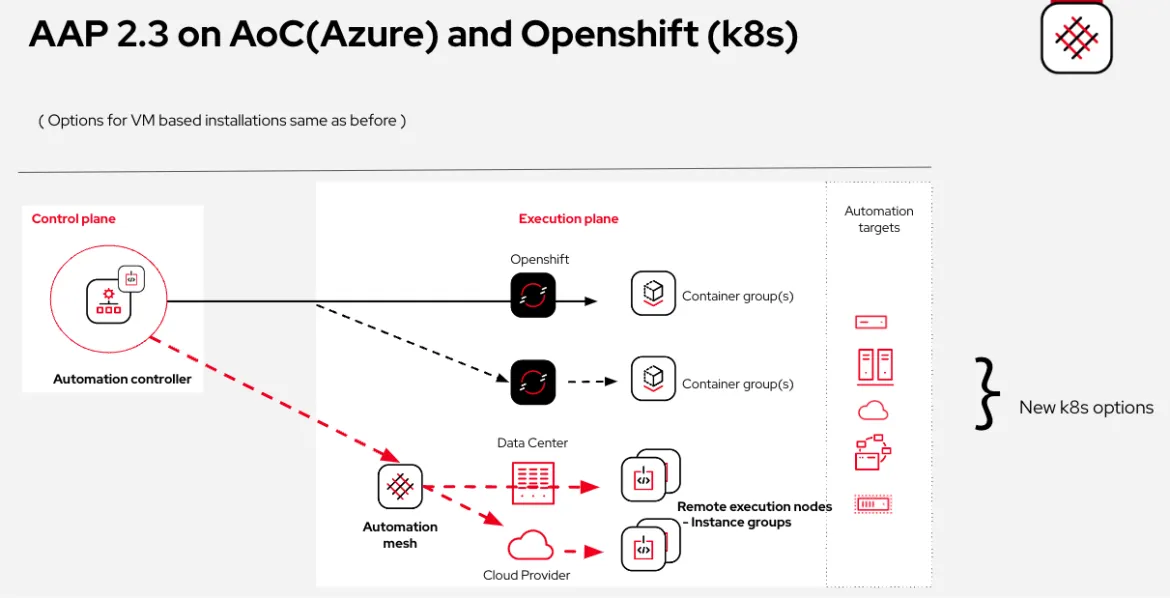
In order to remove this limitation, in AAP 2.3 we have now released in Tech Preview, the ability to add remote mesh execution nodes. This is in addition to the use of the existing container groups.
NOTE: While we have added remote mesh execution nodes, hop nodes are not currently supported. We are working to add this further enhancement during a future release.
During AnsibleFest 2022, our very own controller lead engineer Hao Liu presented a virtual session around adding remote execution nodes when running AAP within a Red Hat OpenShift cluster. The virtual session is free and available on demand and includes more detailed content on how to successfully add remote execution nodes.
In summary
Red Hat Openshift now has the ability to use both container groups and remote execution nodes for automation, which:
- eases resources on the control plane (uwsgi, task manager).
- enables scaling beyond the cluster(s).
Integrate your Red Hat OpenShift AAP deployment with external execution nodes hosted anywhere/any environment:
- on premise data centers.
- cloud providers.
- edge deployments.
What can I do next?
Whether you are beginning your automation journey or a seasoned veteran, there are a variety of resources available to help you get the most out of your automation with Red Hat Ansible.
- If you’re looking for some additional context on the 2.3 release, you can register for our free webinar, “Ansible Automation Platform 2.3: Flexible, trusted automation at scale.”
- Watch the on-demand AnsibleFest 2022 session detailing the adding of remote execution nodes to an AAP on Red Hat OpenShift cluster
- Get hands on with on-demand self-paced exercises - We have a variety of interactive in-browser exercises that have been built to help you dive into directly Ansible Automation Platform.
- Trial subscription - Are you ready to install on-premises? Get your own trial subscription for unlimited access to all the components of Ansible Automation Platform.
- Developer license - Did you know that you can get a free developer license to learn in your home lab? Register and get access to all the latest tools, technologies and community that Red Hat has to offer.
- Subscribe to the Ansible Automation Platform YouTube channel.
- Follow Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform on Twitter - Do you have questions or an automation project you want to show off? Tweet at us!
关于作者
Phil Griffiths is a Product Manager for Ansible Automation Platform with nearly seven years of experience at Red Hat. Phil has held roles as a solution architect and technical consultant both at Red Hat and for other organizations.
产品
工具
试用购买与出售
沟通
关于红帽
我们是世界领先的企业开源解决方案供应商,提供包括 Linux、云、容器和 Kubernetes。我们致力于提供经过安全强化的解决方案,从核心数据中心到网络边缘,让企业能够更轻松地跨平台和环境运营。

