In the previous post the internals of the vDPA kernel framework were covered. Putting the theory aside, the proof is in the pudding so now it’s time to get our hands dirty and try vDPA out. The obvious issue is the vDPA is a HW based feature requiring vendor NICs that support it. So how can we test vDPA when we don’t have such cards? What can we use instead of real hardware?
|
Please note: If your kernel version is newer than v5.19-rc1, please refer to the updated version of this article. |
The answer is a vDPA simulator. The vDPA simulator is a software test device with an IOMMU that is “emulated on a chip.” The vDPA device simulator will loopback TX traffic to its RX. The main use cases for the simulated device are feature testing, prototyping and development. With this simulated device, you can set up your own vDPA test/development environment in minutes!
The following diagram shows the building blocks of a vDPA simulator device:
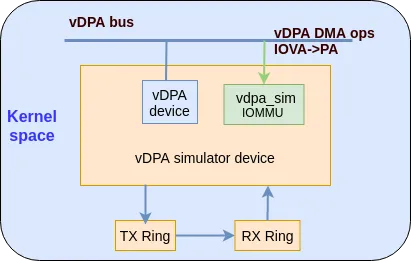
We can use two types of vDPA bus to set up the environment: vhost_vdpa bus driver and virtio_vdpa bus driver. For additional information on these bus drivers refer to (vDPA bus drivers for kernel subsystem interactions).
So in this blog, these are two different scenarios. For use case A: vhost_vdpa will work as a network backend for VM with guest kernel virtio-net driver. For use case B: virtio_vdpa bus will work as a virtio device.
General Requirements
In order to run the vDPA setups the following requirements are mandatory:
-
A computer(Physical machine, VM, container) running a Linux distribution. This guide is focused on Fedora 32, however the commands should not change significantly for other Linux distros
-
A user with
sudopermissions -
About 25GB of free space in your home directory
-
At least 8GB of RAM
-
Your kernel should be 5.4 or above
Use Case A: Experimenting with vhost_vdpa bus driver
Overview of the datapath
The vhost vDPA bus driver connects the vDPA bus to the vhost subsystem and presents a vhost char device to userspace. The vhost-vdpa device could be used as a network backend for VMs with the help of QEMU. For more information see the following blog.
We will use QEMU and a VM to set up this environment.
The following diagram shows the datapath for this solution:
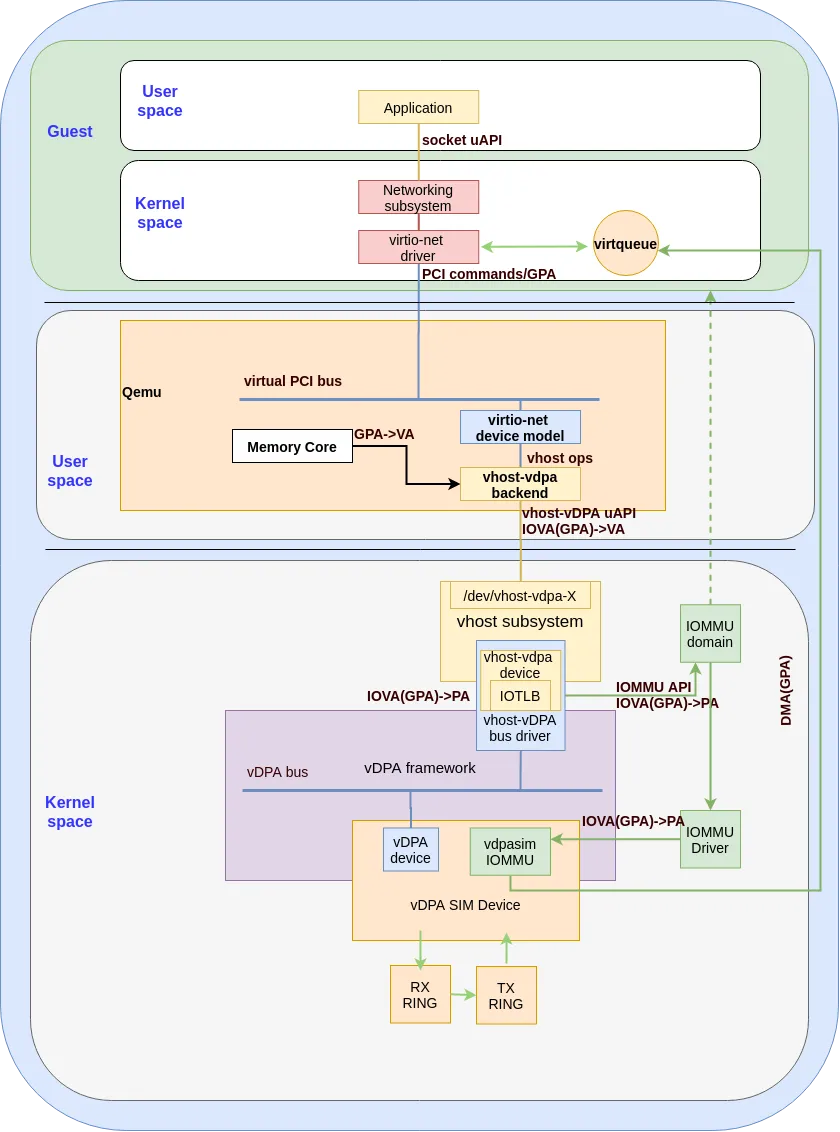
Setting up your environment
Creating a VM
1. Download the latest Fedora-Cloud-Base image: The website for Fedora's Cloud Base Images is https://alt.fedoraproject.org/cloud/. If the download link below is not available, please refer to this website and get a new one:
[user@host ~]# wget https://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/fedora/linux/releases/32/Cloud/x86_64/images/Fedora-Cloud-Base-32-1.6.x86_64.qcow2
2. Prepare the qcow2 image: Use the cleaning command install the related package and change the password to your own:
[user@host ~]# sudo virt-sysprep --root-password password:changeme --uninstall cloud-init --network --install ethtool,pciutils,kernel-modules-internal --selinux-relabel -a Fedora-Cloud-Base-32-1.6.x86_64.qcow2
Compile the kernel
For some linux distros, the vDPA kernel framework was not enabled by default, we need to download the linux source code and compile it. Below are the steps to compile the linux kernel. (The kernel version should be 5.4 or above)
You can get more information about how to compile linux kernels from how-to-compile-linux-kernel. You can skip this part if you are familiar with it.
[user@host ~]# git clone git://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/torvalds/linux.git [user@host ~]# cd linux [user@host ~]# git checkout v5.8 [user@host ~]# cp /boot/config-$(uname -r) .config [user@host ~]# vim .config (please refer to the note about enabling the vDPA kernel framework) [user@host ~]# make -j [user@host ~]# sudo make modules_install [user@host ~]# sudo make install
And reboot to the newly installed kernel.
Note: We need to set the following lines in the .config file to enable vDPA kernel framework:
CONFIG_VIRTIO_VDPA=m CONFIG_VDPA=y CONFIG_VDPA_SIM=m CONFIG_VHOST_VDPA=m
Note: If you prefer to use make menuconfig, you can find these options under section Device Drivers, named DPA drivers, Virtio drivers and VHOST drivers as kernel 5.8.
Compile and install QEMU
1. Download the qemu code: The support for vhost-vdpa backend was merged in v5.1.0 thus you should use that version or above:
[user@host ~]# git clone https://github.com/qemu/qemu.git
2. Compile the qemu: Follow the commands below (see the README.rst in qemu for more information):
[user@host ~]# cd qemu/ [user@host ~]# git checkout v5.1.0-rc3 [user@host ~]# mkdir build [user@host ~]# cd build/ [user@host ~]#../configure --enable-vhost-vdpa --target-list=x86_64-softmmu [user@host ~]# make
Configuring the host
1. Load all the related kmod: You should now load the kmod with the following commands:
[user@host ~]# modprobe vdpa [user@host ~]# modprobe vhost_vdpa [user@host ~]# modprobe vdpa_sim
2. Verify vhost_vdpa is loaded correctly: Ensure the bus driver is indeed vhost_vdpa using the following commands:
[user@host ~]# ls -l /sys/bus/vdpa/drivers drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 0 Sep 5 16:54 vhost_vdpa #ls -l /sys/bus/vdpa/devices/vdpa0/ total 0 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 0 Sep 21 12:24 driver -> ../../bus/vdpa/drivers/vhost_vdpa drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 0 Sep 21 12:25 power lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 0 Sep 21 12:25 subsystem -> ../../bus/vdpa -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 4096 Sep 21 12:24 uevent drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 0 Sep 21 12:25 vhost-vdpa-0 [user@host ~]# ls -l /dev/ |grep vdpa crw------- 1 root root 239, 0 Sep 5 16:54 vhost-vdpa-0
3. Set the ulimit -l unlimited: ulimit -l means the maximum size that may be locked into memory. In this case we need to set it to unlimited, since vhost-vDPA needs to lock pages for making sure the hardware DMA works correctly:
[user@host ~]# ulimit -l unlimited
if you forget to set this, you may get the error message from qemu similar to this:
qemu-system-x86_64: failed to write, fd=12, errno=14 (Bad address) qemu-system-x86_64: vhost vdpa map fail! qemu-system-x86_64: vhost-vdpa: DMA mapping failed, unable to continue
4. Launch the guest VM: The device /dev/vhost-vdpa-0 is the vDPA device we can use. This is a simple example of using QEMU to launch a VM with vhost_vdpa:
[user@host ~]# sudo x86_64-softmmu/qemu-system-x86_64 \ -hda Fedora-Cloud-Base-32-1.6.x86_64.qcow2 \ -netdev type=vhost-vdpa,vhostdev=/dev/vhost-vdpa-0,id=vhost-vdpa1 \ -device virtio-net-pci,netdev=vhost-vdpa1,mac=00:e8:ca:33:ba:05,\ disable-modern=off,page-per-vq=on \ -enable-kvm \ -nographic \ -m 2G \ -cpu host \ 2>&1 | tee vm.log
5. Verify the port was created successfully: After the guest boots up, we can then login in to it. We should verify that the port has been bounded successfully to the virtio driver. This is since the backend of the virtio_net driver is vhost_vdpa and if something went wrong the driver will not be created.
guest login: root Password: Last login: Tue Sep 29 12:03:03 on ttyS0 [root@guest ~]# ip -s link show eth0 2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP mode DEFAULT gro0 link/ether fa:46:73:e7:7d:78 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff RX: bytes packets errors dropped overrun mcast 12006996 200043 0 0 0 0 TX: bytes packets errors dropped carrier collsns 12006996 200043 0 0 0 0 [root@guest ~]# ethtool -i eth0 **driver: virtio_net** version: 1.0.0 firmware-version: expansion-rom-version: bus-info: 0000:00:04.0 supports-statistics: yes supports-test: no supports-eeprom-access: no supports-register-dump: no supports-priv-flags: no [user@guest ~]# lspci |grep 00:04.0 00:04.0 Ethernet controller: Red Hat, Inc. Virtio network device
Running traffic with vhost_vdpa
Now that we have a vdpa_sim port with the loopback function. we can generate traffic using pktgen to verify it. Pktgen is a packet generator integrated with Linux kernel. For more information please refer to the pktgen doc and sample test script.
[root@guest ~]# ip -s link show eth0 2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP mode DEFAULT gro0 link/ether fa:46:73:e7:7d:78 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff RX: bytes packets errors dropped overrun mcast 18013078 300081 0 0 0 0 TX: bytes packets errors dropped carrier collsns 18013078 300081 0 0 0 0 [root@guest ~]# ./pktgen_sample01_simple.sh -i eth0 -m 00:e8:ca:33:ba:05 (you can get this script from sample test script) [root@guest ~]# ip -s link show eth0 2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP mode DEFAULT gro0 link/ether fa:46:73:e7:7d:78 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff RX: bytes packets errors dropped overrun mcast 24013078 400081 0 0 0 0 TX: bytes packets errors dropped carrier collsns 24013078 400081 0 0 0 0
You can see the RX packets are increasing together with TX packets which means that vdpa_sim is working as expected.
Use Case B: Experimenting with virtio_vdpa bus driver
Overview of the datapath
The virtio_vdpa driver is a transport implementation for kernel virtio drivers on top of vDPA bus operations. The virtio_vdpa driver will create a virtio device in the virtio bus. For more information on the virtio_vdpa bus see here.
The following diagram shows the datapath for virtio-vDPA using a vdpa_sim (the vDPA simulator device):
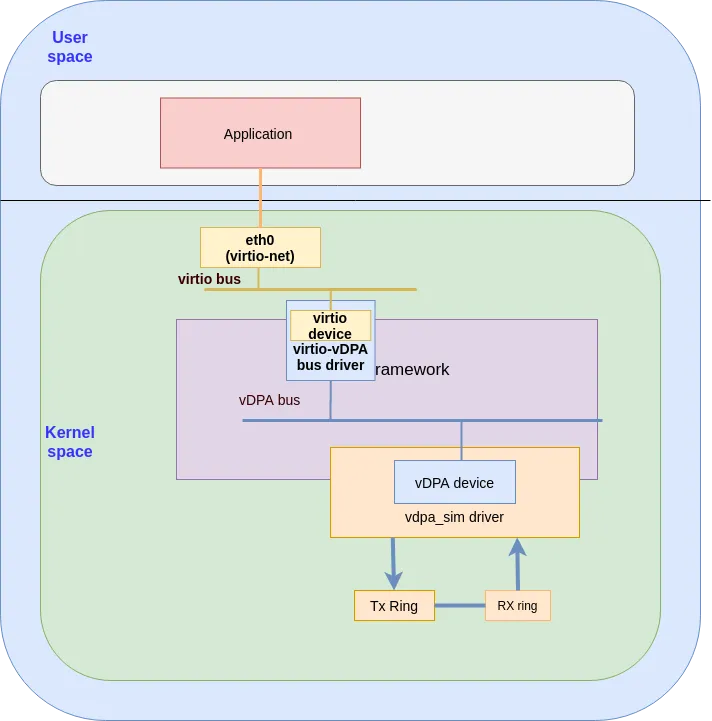
Setting up your environment
1. Load the modules
[user@host ~]# modprobe vdpa [user@host ~]# modprobe virtio_vdpa [user@host ~]# modprobe vdpa_sim
Note: if the vDPA related modules are not compiled then follow the instructions in Use Case A vhost_vpda bus driver to compile them.
2. Verify virtio_vdpa loads correctly
[user@host ~]# lsmod |grep vdpa_sim vdpa_sim 16384 0 vringh 28672 1 vdpa_sim vhost_iotlb 16384 2 vdpa_sim,vringh vdpa 16384 2 vdpa_sim,virtio_vdpa
3. Verify the driver is bounded to virtio-vdpa correctly
[user@host ~]# ls -l /sys/bus/vdpa/devices/vdpa0/ total 0 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 June 23 11:19 driver -> ../../bus/vdpa/drivers/virtio_vdpa drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 0 June 23 11:19 power lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 June 23 11:19 subsystem -> ../../bus/vdpa -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4096 June 23 11:19 uevent drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 0 June 23 11:19 virtio0
4. Switching from a vhost_vdpa to virtio_vdpa if needed
If in step 4 you see that the interface is bounded to vhost_vdpa instead of virtio_vdpa we need to switch it to virtio_vdpda using the following instructions:
[user@host ~]# echo vdpa0 > /sys/bus/vdpa/drivers/vhost_vdpa/unbind [user@host ~]# echo vdpa0 > /sys/bus/vdpa/drivers/virtio_vdpa/bind [user@host ~]# ls -l /sys/bus/vdpa/devices/vdpa0/ total 0 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 June 23 11:19 driver -> ../../bus/vdpa/drivers/virtio_vdpa drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 0 June 23 11:19 power lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 June 23 11:19 subsystem -> ../../bus/vdpa -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4096 June 23 11:19 uevent drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 0 June 23 11:19 virtio0
You should get the same output for the ls command as shown in this example.
5. Verify the bus-info
Now we want to confirm that everything is configured properly and for that we want to ensure our port uses a bus-info of type vdpa:
[user@host ~]# ip -s link show eth0 6: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP mode DEFAULT gro0 link/ether f6:8c:ea:ac:e6:8d brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff RX: bytes packets errors dropped overrun mcast 137438 803 0 0 0 0 TX: bytes packets errors dropped carrier collsns 137438 803 0 0 0 0 [user@host ~]# dnf install ethtool [user@host ~]# ethtool -i eth0 driver: virtio_net version: 1.0.0 firmware-version: expansion-rom-version: bus-info: vdpa0 supports-statistics: yes supports-test: no supports-eeprom-access: no supports-register-dump: no supports-priv-flags: no
Running traffic on the virtio_vdpa
Now that we have a vdpa_sim port with the loopback function. Just like in Use Case A: vhost-vdpa, we can generate traffic using pktgen to verify it. If the pktgen was not installed, you can install it by following command.
[user@host ~]# dnf install kernel-modules-internal
For more information please refer to the pktgen doc and sample test script.
Following are the commands and the running logs:
[user@host ~]# ip -s link show eth0 6: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP mode DEFAULT gro0 link/ether f6:8c:ea:ac:e6:8d brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff RX: bytes packets errors dropped overrun mcast 6227004 101327 0 0 0 0 TX: bytes packets errors dropped carrier collsns 6227004 101327 0 0 0 0 [user@host ~]# ./pktgen_sample01_simple.sh -i eth0 -m 00:e8:ca:33:ba:05 (you can get this script from sample test script) [user@host ~]# ip -s link show eth0 6: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP mode DEFAULT gro0 link/ether f6:8c:ea:ac:e6:8d brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff RX: bytes packets errors dropped overrun mcast 12227330 201328 0 0 0 0 TX: bytes packets errors dropped carrier collsns 12227330 201328 0 0 0 0
You can see the RX packets are increasing together with TX packets which means the vdpa_sim is working as expected.
Summary
In this blog we’ve guided you on how to set up a vDPA testing environment without using vDPA HW. We’ve covered both the virtio_vdpa bus and the vhost_vdpa bus.
We hope this helped make these concepts more real and grounded them in actual Linux tooling.
To keep up with the virtio-networking community we invite you to sign up to the virtio-networking mailing list. This is a public mailing list, and you can register through the Mailman page.
Sugli autori
Cindy is a Senior Software Engineer with Red Hat, specializing in Virtualization and Networking.
Experienced Senior Software Engineer working for Red Hat with a demonstrated history of working in the computer software industry. Maintainer of qemu networking subsystem. Co-maintainer of Linux virtio, vhost and vdpa driver.
Altri risultati simili a questo
Ricerca per canale
Automazione
Novità sull'automazione IT di tecnologie, team e ambienti
Intelligenza artificiale
Aggiornamenti sulle piattaforme che consentono alle aziende di eseguire carichi di lavoro IA ovunque
Hybrid cloud open source
Scopri come affrontare il futuro in modo più agile grazie al cloud ibrido
Sicurezza
Le ultime novità sulle nostre soluzioni per ridurre i rischi nelle tecnologie e negli ambienti
Edge computing
Aggiornamenti sulle piattaforme che semplificano l'operatività edge
Infrastruttura
Le ultime novità sulla piattaforma Linux aziendale leader a livello mondiale
Applicazioni
Approfondimenti sulle nostre soluzioni alle sfide applicative più difficili
Serie originali
Raccontiamo le interessanti storie di leader e creatori di tecnologie pensate per le aziende
Prodotti
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux
- Red Hat OpenShift
- Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform
- Servizi cloud
- Scopri tutti i prodotti
Strumenti
- Formazione e certificazioni
- Il mio account
- Supporto clienti
- Risorse per sviluppatori
- Trova un partner
- Red Hat Ecosystem Catalog
- Calcola il valore delle soluzioni Red Hat
- Documentazione
Prova, acquista, vendi
Comunica
- Contatta l'ufficio vendite
- Contatta l'assistenza clienti
- Contatta un esperto della formazione
- Social media
Informazioni su Red Hat
Red Hat è leader mondiale nella fornitura di soluzioni open source per le aziende, tra cui Linux, Kubernetes, container e soluzioni cloud. Le nostre soluzioni open source, rese sicure per un uso aziendale, consentono di operare su più piattaforme e ambienti, dal datacenter centrale all'edge della rete.
Seleziona la tua lingua
Red Hat legal and privacy links
- Informazioni su Red Hat
- Opportunità di lavoro
- Eventi
- Sedi
- Contattaci
- Blog di Red Hat
- Diversità, equità e inclusione
- Cool Stuff Store
- Red Hat Summit

