Our previous two blogs discussed the TMForum Intelligent edge for sustainable agriculture - phase II catalyst project. The project's goal is to reimagine and streamline sustainable agriculture practices at the edge.
Our first blog discussed the role of 5G, edge, artificial intelligence (AI) and an open source cloud-native platform to provide real-time insights that would enable precision agriculture. Our second blog outlined the importance of a sustainability-first design principle and holistic approach to target the reduction of energy consumption and carbon emissions.
Here we will discuss the role of different types of AI, highlighting how generative AI (GenAI) can be applied to this catalyst project to improve results. The catalyst project utilizes both traditional and GenAI to enhance the context and usability of information directly attributed to increased productivity and efficiency for precision farming.
GenAI is also used to enhance the usability of the data and graphics processing unit (GPU) power efficiency in our sustainability models, as we outlined in our second blog, and positively impacts a number of United Nations defined sustainability goals (UN SDGs).
What is GenAI and an AI Platform?
A comprehensive AI and machine learning (AI/ML) approach derives varied data that gives improved context, insights, and, ultimately, outcomes. GenAI relies on deep learning models trained on large data sets to create new content to enhance the analysis. Deep learning models recreate patterns they've learned from a vast amount of training data and work within human-constructed parameters to make something new based on what they've learned.
Red Hat OpenShift is a key component of the open solution blueprint that has been developed for this catalyst project. As shown in Figure 1, Red Hat OpenShift AI, driven by open source innovation, leverages application development and deployment platform capabilities as the catalyst for AI workloads to build, train, tune and serve AI models at scale. These capabilities accelerate the infusion of AI/ML into applications, services and business operations regardless of their location in the network. By leveraging OpenShift as the unifying platform, GenAI capabilities can be more easily injected and deployed across the solution.
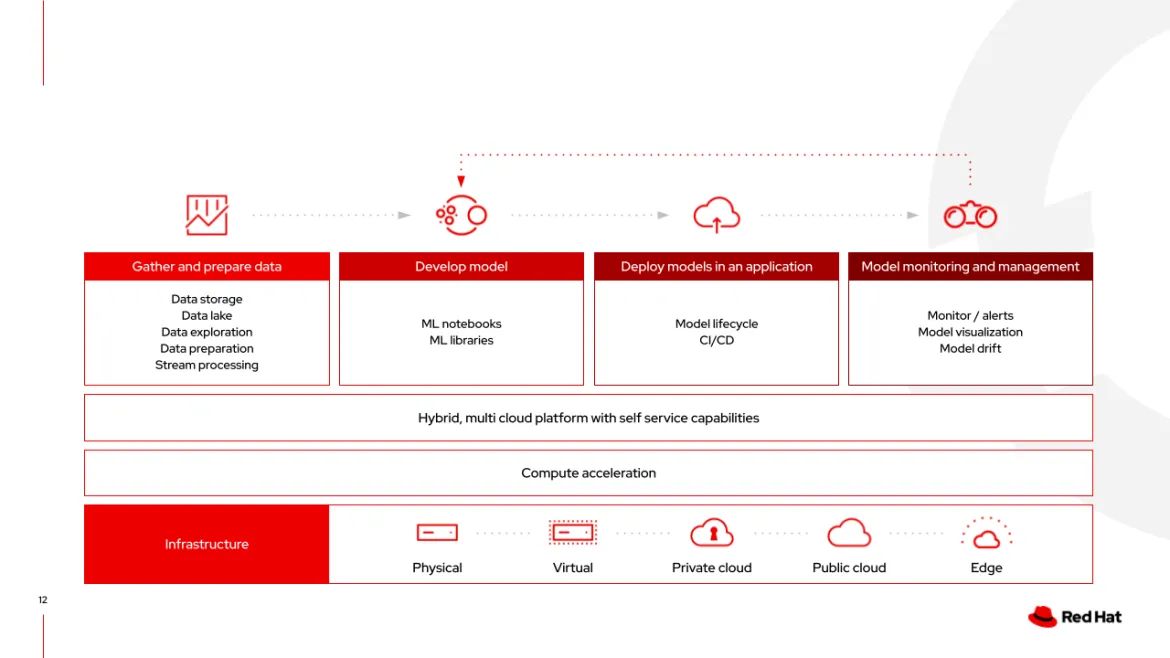
Figure 1: Red Hat OpenShift AI for the consistent development and deployment of AI-enabled applications across hybrid cloud
GenAI at the edge for precision farming: Soil health management
Our intelligent edge for sustainable agriculture catalyst creates an open blueprint and flexible framework for GenAI applications to operate from the Farm Edge back to core technology data centers. As shown in Figure 2, the catalyst relies upon the constant creation, flow and ingestion of data. This data ecosystem starts with Red Hat Device Edge, which uses the power of open source and open application programming interfaces (APIs) to address diverse environmental constraints and physical footprints and provides real time, informed decision-making essential for proactive soil health management.
Farm Edge Mid Edge - Regional Core Cloud
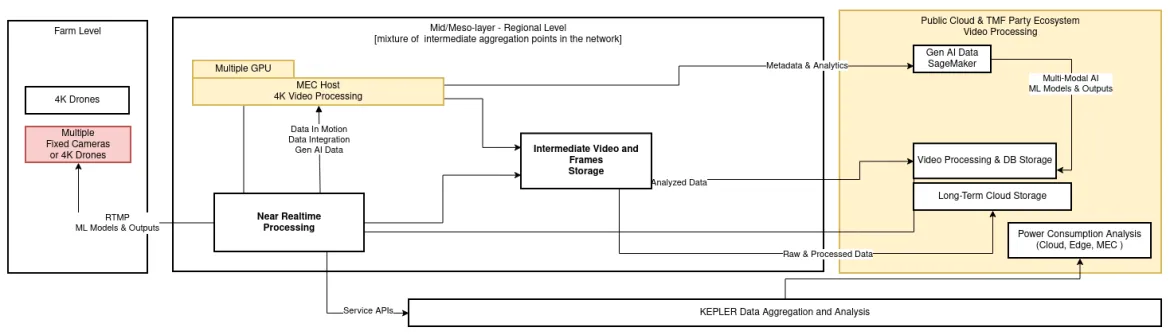
Figure 2: Holistic data integration framework across the network
Red Hat Device Edge provides hybrid cloud open source technology and enterprise automation to remote sites. Amazon Web Services (AWS) Greengrass is installed and combined as part of the Red Hat Device Edge image. This edge solution acts as a gateway and processing center to send data back to the core data center and apply data inference locally. It is crucial in making a range of AI data available for GenAI models and applications for the catalyst.
As data travels from the edge, it consumes high-power graphical processing unit (GPU) services offered by the 5G multiaccess edge compute (MEC) host running on OpenShift. As shown in Figure 3, traditional data science models using Red Hat OpenShift AI with a Jupyter notebook and no-code GenAI applications, such as flowise and langflow, demonstrate the variety of open source tools available for deployment. The MEC host offers flexibility and the necessary security required to process GPU and compute-intensive data within an environment that's typically much larger than the device edge.
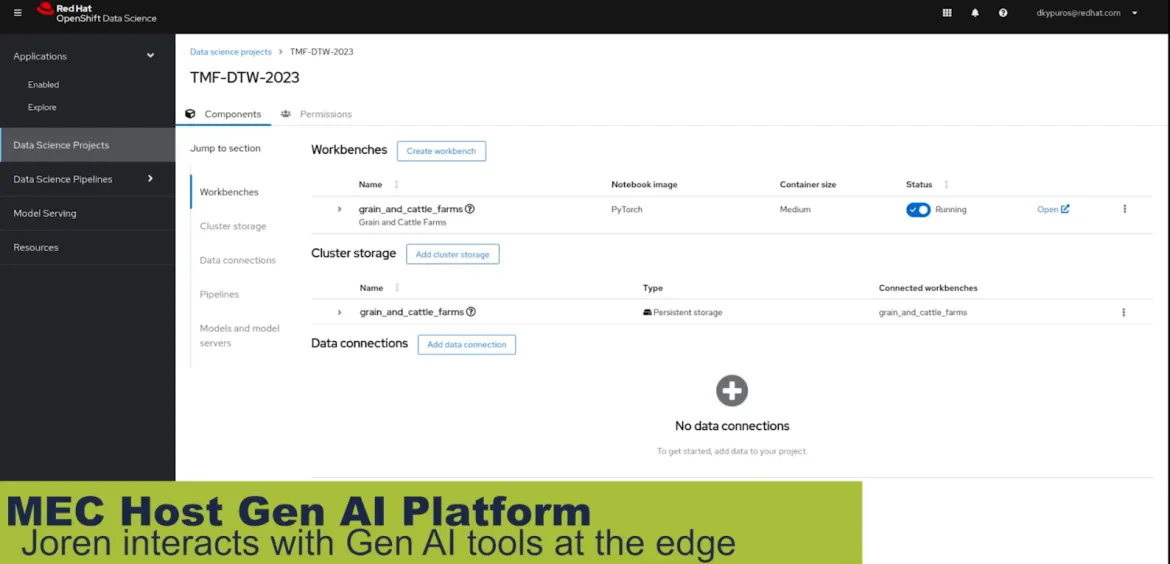
Figure 3: The role of MEC for GenAI-infused capabilities
As shown in Figure 4, a GenAI chatbot can "talk to the soil" to help farmers analyze, learn and ask questions about their overall soil conditions. This feature is a direct result of enabling AI from the device edge toward the core data center. The near real-time access to such data is significant for the farmer when paired with a digital twin solution like the one shown here from AWS.
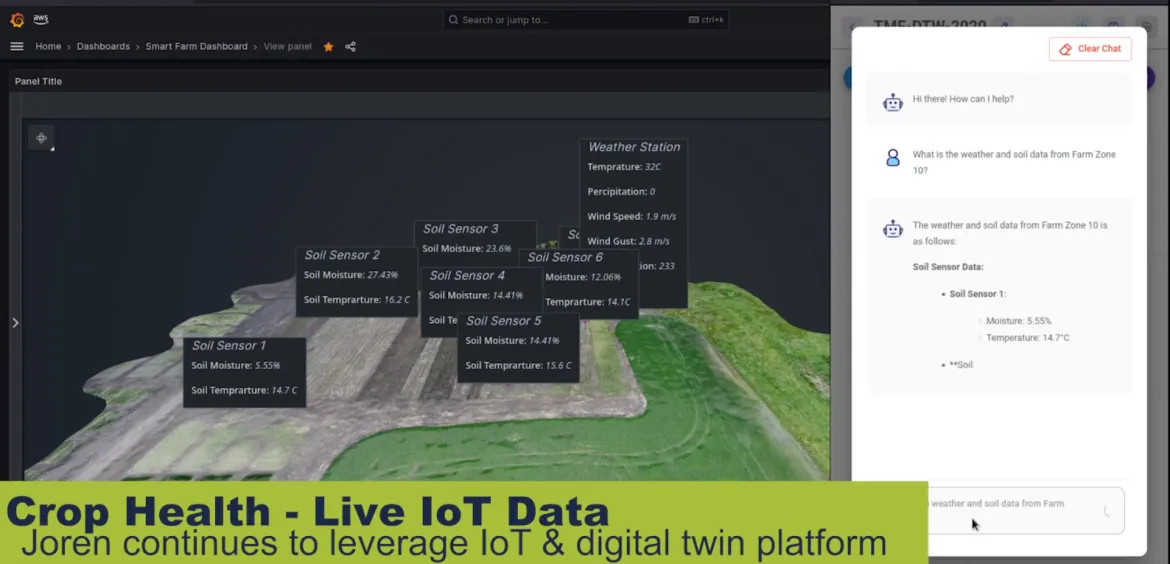
Figure 4: Precision farming GenAI chatbot
GenAI at the edge for precision farming: Crop health monitoring
AI and computer vision are revolutionizing the agricultural industry. Images and videos are captured by drones flying about 10 meters above crop fields equipped with high-resolution cameras and global positioning system (GPS) capabilities. The data is analyzed through image preprocessing techniques such as normalization, resizing and augmentations.
As shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6, a deep learning model trained on a diverse dataset of healthy and stressed crops accurately segments and classifies crops. The identified areas are geo-located, and the information is integrated with existing farm management systems. This brings numerous benefits, such as enabling precise identification of stressed plants for targeted treatments, optimizing resource use, aiding in harvest scheduling and offering scalability to other crops and environments.
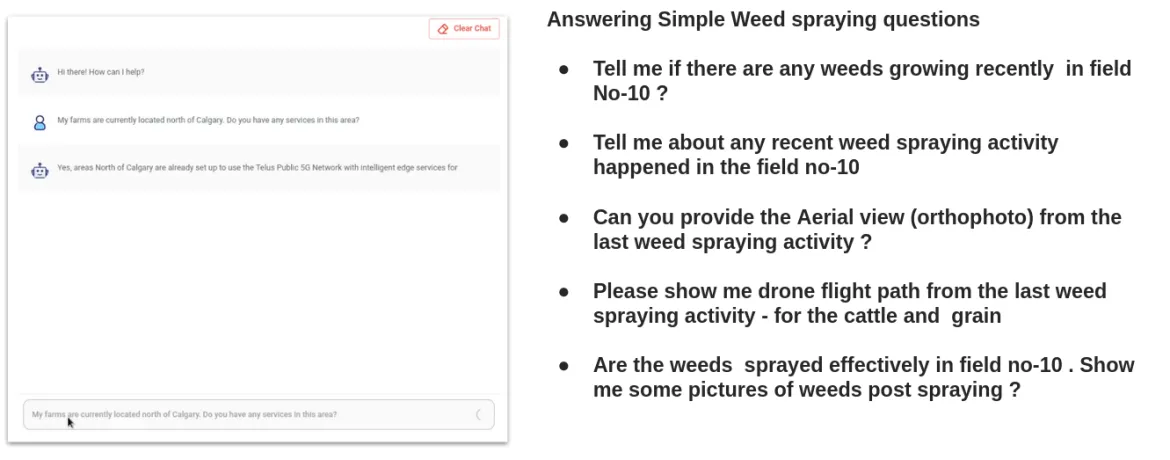
Figure 5: Image processing of crop health GenAI allows farmers to respond to the weed data
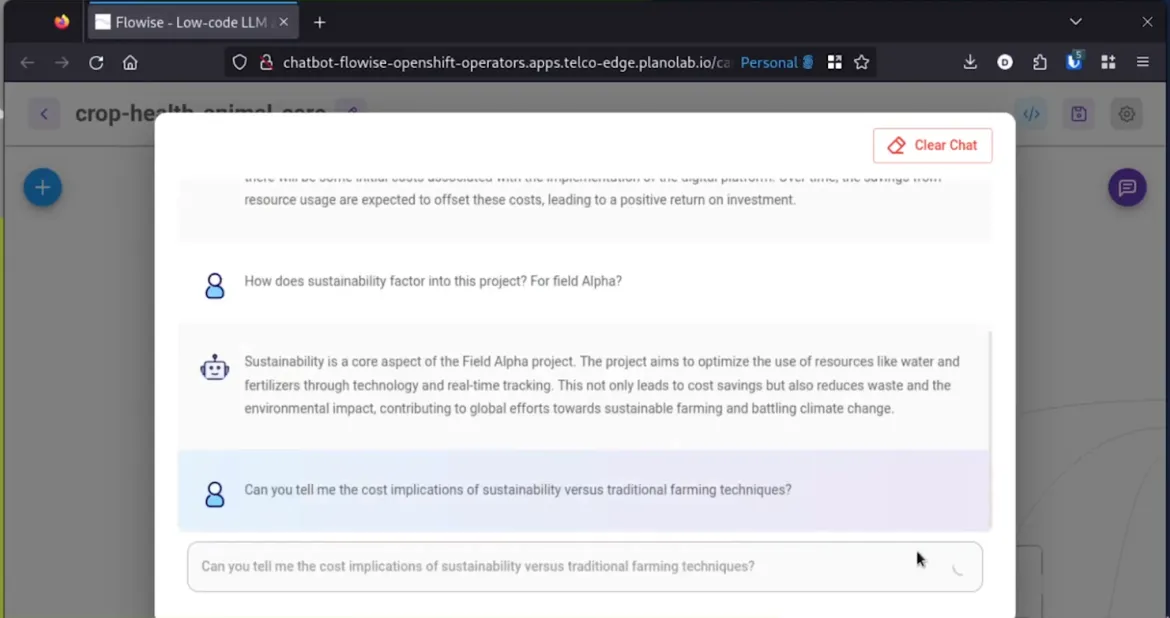
Figure 6: Crop health-related data can be aggregated and made accessible via a ChatBot to the farmer
Our involvement with this catalyst project has simplified the use of AI with edge technologies to drive enhanced benefits for precision farming. Benefits include:
- Reduction of fertilizer usage by 20% with the removal of indiscriminate spraying practices.
- Reduction of water consumption by 30% with efficient irrigation from machine learning techniques that develop crop-based watering need models across the growing season.
- Up to 50% in time savings in farm operations by utilizing computer vision and camera footage that creates immediate and actionable alerts.
When you combine an open framework that enables AI to access data, deploy GenAI applications, and operate workloads across various platforms, you have a solution that provides real business impact to the agriculture industry. Each tier of the framework, from the data-rich edge to agriculture dashboards in the cloud, works in concert to address the specific business challenges farmers face in managing their day-to-day operations.
We believe that open source communities are where innovation happens, which is especially true of AI, including the emergence of GenAI. Our upstream-first approach allows us to foster open, transparent contributions that position us to deliver those innovations toward downstream AI products for customers and partners.
Red Hat OpenShift AI provides the foundation for building and deploying AI applications and machine learning (ML) models with transparency, control and a more unified user experience.
Red Hat and OpenShift are recognized by TelecomTV as the cloud-native telecommunications market leaders for 5G due to their long-standing commitment to open source. As we outlined in our second blog, driving open source projects on sustainability and power monitoring and using these capabilities with OpenShift AI for metrics reporting make OpenShift a clear choice for organizations to better achieve their sustainability needs.
Red Hat also uses its own OpenShift AI tools to improve the usability of other open source software, starting with Ansible Lightspeed with IBM watsonx Code Assistant. Ansible Lightspeed with IBM watsonx Code Assistant helps developers create Ansible content more efficiently, translating plain English to Ansible language using the IBM watsonx foundation model.
To learn more, see Red Hat OpenShift, Red Hat OpenShift AI and Ansible Lightspeed with IBM watsonx Code Assistant, and read the resources located at the TMForum website.
저자 소개
Rob McManus is a Principal Product Marketing Manager at Red Hat. McManus is an adept member of complex matrix-style teams tasked to define and position telecommunication service provider and partner solutions with a focus on network transformation that includes 5G, vRAN and the evolution to cloud-native network functions (CNFs).
Rich Gee is Head of 5G Sales at Red Hat. He leads global sales and business development focused on collaboration with customers in the telecommunications network and edge transformation, incubating emerging technologies and developing forward-looking solutions to generate new revenue. Prior to joining Red Hat in 2016, Gee was Director, OEM Sales at MicroStrategy, an analytics software company.
He has more than 30 years of experience in the enterprise software and information technology field as Director, Global Sales and Business Development at Sun, Oracle and Mellanox with over 20 years focused in the telecommunications industry. He has also previously developed emerging sales in the Industrial/Semiconductor, Retail and Consumer Electronics sectors. He is passionate about open source and community source software delivering next generation changes in broad markets and industries.
David Kypuros is a Global Principal Solutions Architect at Red Hat. With over 15 years in telecommunications, including pivotal roles at Verizon and AT&T, David now leads initiatives in 5G, edge computing, and AI. A key contributor to the TM Forum Catalyst programs, David has earned accolades for leading award-winning projects in sustainability and generative AI, underscoring a commitment to innovative and responsible technology solutions.
채널별 검색
오토메이션
기술, 팀, 인프라를 위한 IT 자동화 최신 동향
인공지능
고객이 어디서나 AI 워크로드를 실행할 수 있도록 지원하는 플랫폼 업데이트
오픈 하이브리드 클라우드
하이브리드 클라우드로 더욱 유연한 미래를 구축하는 방법을 알아보세요
보안
환경과 기술 전반에 걸쳐 리스크를 감소하는 방법에 대한 최신 정보
엣지 컴퓨팅
엣지에서의 운영을 단순화하는 플랫폼 업데이트
인프라
세계적으로 인정받은 기업용 Linux 플랫폼에 대한 최신 정보
애플리케이션
복잡한 애플리케이션에 대한 솔루션 더 보기
오리지널 쇼
엔터프라이즈 기술 분야의 제작자와 리더가 전하는 흥미로운 스토리
제품
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux
- Red Hat OpenShift Enterprise
- Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform
- 클라우드 서비스
- 모든 제품 보기
툴
체험, 구매 & 영업
커뮤니케이션
Red Hat 소개
Red Hat은 Linux, 클라우드, 컨테이너, 쿠버네티스 등을 포함한 글로벌 엔터프라이즈 오픈소스 솔루션 공급업체입니다. Red Hat은 코어 데이터센터에서 네트워크 엣지에 이르기까지 다양한 플랫폼과 환경에서 기업의 업무 편의성을 높여 주는 강화된 기능의 솔루션을 제공합니다.



