Policy framework and Integrity Shield
The policy framework in Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes is a powerful feature that helps you govern configurations across multiple clusters. Read the Overview blogs for more information about the policy framework.
The integrity of Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management policies is critical because policies may include critical configurations for your clusters and any modification, maliciously or accidentally, can negatively impact your cluster.
Digital signature provides cryptographic assurance for protecting the integrity of data. If we could control requests for policies based on signature verification, it would provide additional forms of protection. Integrity Shield provides preventive control for enforcing signature verification for any requests to create or update Kubernetes resources. You can secure your policies from being maliciously modified by using Integrity Shield.
In this blog, I will introduce three great advantages that are available in the new release of Integrity Shield version 0.3.2, which is technical preview availability for the recent Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management 2.4 release. To learn more, visit Integrity Shield.
sigstore support
First, there is a major update regarding supported signature types. In addition to PGP and x509 signing, Integrity Shield now supports the signing for Kubernetes manifests with sigstore, an open source project that has been getting a lot of attention recently. This new capability is achieved by using the core verification mechanism of k8s-manifest-sigstore, which is one of the subprojects in the sigstore community. With this update, you can now use various signatures, including support for keyless signing.
Monitoring to check policy protection
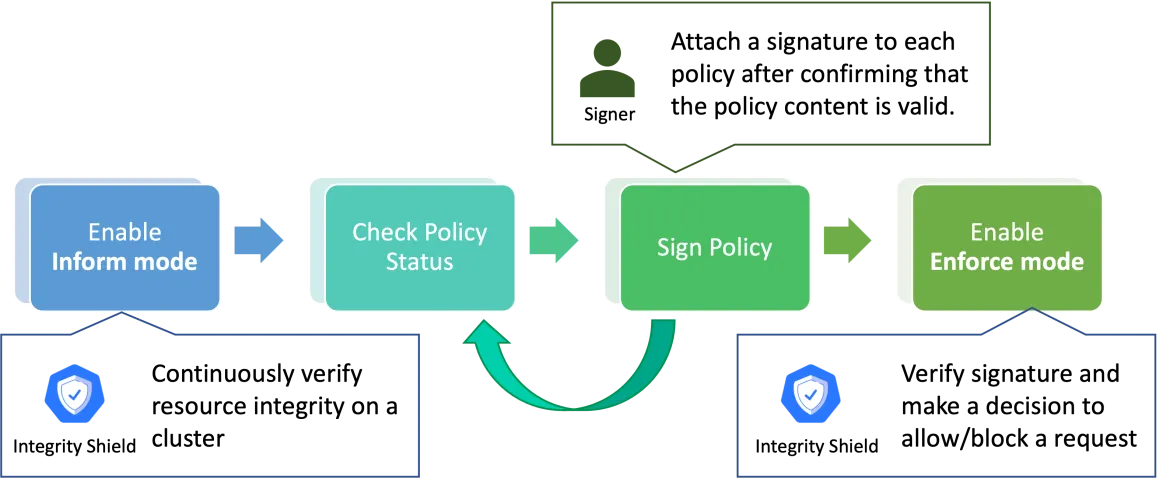
Next, the new Integrity Shield release provides a monitoring feature that allows you to check the policy protection status on the cluster in inform mode before enabling enforcement. In inform mode, Integrity Shield monitors the integrity of Kubernetes resources and reports if any unauthorized Kubernetes resources are deployed on a cluster, instead of preventing the installation of unauthorized requests. So, you can use the protection feature in phases as desired. The following diagram illustrates this phased approach. In particular, first you can apply the protection in inform mode to check the cluster integrity status and resolve it if there are any violations. After confirming that the policy content is valid and attaching a signature to all policies, you can switch to enforce mode to protect the cluster more robustly. In enforce mode, Integrity Shield provides preventive control for enforcing signature verification for any requests to create or update resources. This means that Integrity Shield blocks any request without a signature to create and update resources. Since detect mode only monitors existing policies and does not affect them, it is easier to apply Integrity Shield validation features.
Integrity Shield API and Integrity Shield Observer
Finally, if you are already using OPA/Gatekeeper, you can enable this powerful protection by simply installing some components: Integrity Shield API and Integrity Shield Observer.
These components can be easily installed from Operatorhub.io: K8s Integrity Shield by using a policy for Integrity Shield. Gatekeeper is an admission controller that enforces CRD-based policies executed by Open Policy Agent. It is already integrated with Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management policy framework, so the installation of OPA/Gatekeeper is seamless. Since Integrity Shield works with OPA/Gatekeeper, you can configure protection rules based on the OPA/Gatekeeper constraint framework.
Getting Started
Let’s take a look at how to install K8s Integrity Shield by using a custom policy with Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management and how Integrity Shield protects policies with sigstore keyless signing. If you want to try this tutorial using PGP keys, see this document.
Prerequisites
-
You need OPA/Gatekeeper. Before installation, Gatekeeper should be installed on the cluster. The Gatekeeper operator is also integrated with Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management and can be installed by using this policy.
-
You need
k8s-manifest-sigstoreYou need to set up the kubectl plugin for signing Kubernetes manifest YAML files with sigstore. See this instruction. -
You need Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management policies and GitOps. You need to have policies that are already synced between the GitHub repository and clusters. See this Contributing and deploying community policies with Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management and GitOps for more information about setting up GitOps.
Procedure
- Enable your policy on target clusters. We use three policies in the community folder of the policy-collection repository on GitHub to enable Integrity Shield:
- policy-integrity-shield.yaml
- policy-integrity-shield-observer.yaml
- policy-integrity-shield-events.yaml
By default, these policies are deployed in inform mode. The policy policy-integrity-shield.yaml for deploying K8s Integrity Shield should be configured to enable K8s Integrity Shield on target clusters. Set remediationAction in the following specification to enforce:
apiVersion: policy.open-cluster-management.io/v1
kind: Policy
metadata:
name: policy-integrity-shield
annotations:
policy.open-cluster-management.io/standards: NIST SP 800-53
policy.open-cluster-management.io/categories: CM Configuration Management
policy.open-cluster-management.io/controls: CM-5 Access Restrictions for Change
spec:
remediationAction: inform #Change this line to `enforce`.
disabled: false
After configuring policy-integrity-shield, commit and push the policy local changes to the remote repository in order to sync policies with target clusters. Once these policies are distributed to target clusters, Integrity Shield will be installed by Integrity Shield Operator.
The protection rule (ManifestIntegrityConstraint) for Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management policies will also be installed by policy-integrity-shield. Therefore, after installing these policies, the signature-based protection feature is enabled. This rule is set to inform mode initially.
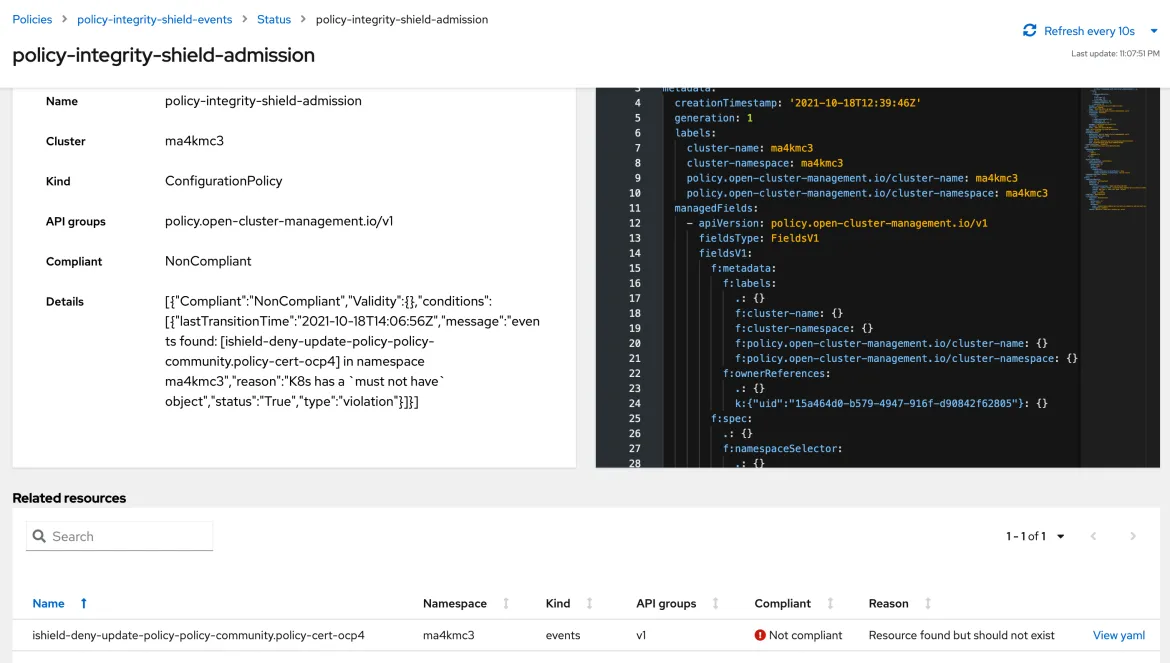
- Check cluster integrity on Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management console. If there are any noncompliant constraints, they will be listed in the console.
Policy-integrity-shield-observer reports whether there are any invalid resources on the target clusters. This policy will be compliant only if all policies are signed. If there is any unsigned policy on the target cluster, the state will be not compliant. Therefore, you can know the status of policies already in the cluster when you enable Integrity Shield from policy-integrity-shield-observer policy. Some Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management policies may not be signed initially, so the policy-integrity-shield-observer policy may not be in a compliant state.
By moving to the details page of the policy-integrity-shield-observer policy, you can check in detail which policy does not have a signature. In the following example, there are four policies that are not signed.
- Sign the policies. Digital signature provides cryptographic assurance for protecting the integrity of data. Let's attach a signature to unsigned policies. The signature for each policy is attached into annotations in the policy manifest.
The following example shows how to sign a policy file policy-xxxxx.yaml using sigstore signing. You can use the kubectl subcommand plugin of k8s-manifest-sigstore to sign a policy. See sigstore /k8s-manifest-sigstore for more details including how to install and configure the plugin.
$ export COSIGN_EXPERIMENTAL=1
$ kubectl sigstore sign -f policy-xxxxx.yaml
The signed YAML policy-xxxxx.yaml.signed is generated by the command. You can confirm the YAML content is signed with the presence of the cosign.sigstore.dev/bundle, cosign.sigstore.dev/certificate, cosign.sigstore.dev/message and cosign.sigstore.dev/signature annotation as shown below:
Then, push the signed policies to your remote repository. Policies can be kept in sync with target clusters automatically using GitOps based tools and strategies if desired.
You should sign all unsigned policies by the steps above for protecting all policies. Once the new policies have been applied, and after a few moments, the policy-integrity-shield-observer policy will be compliant status as all policies on target clusters have valid signatures.
In all above steps, signature is attached into annotations in the policy manifest. In addition to that, the signature can be stored in the OCI registry. To sign a policy manifest using the OCI registry, you can use the following command. In this case, a signature is generated for the manifest image sample-registry/sample-policy-signature:0.0.1, which includes a policy file policy-xxxxx.yaml, and the signed image is pushed to the OCI registry.
$ export COSIGN_EXPERIMENTAL=1
$ kubectl sigstore sign -f policy-xxxxx.yaml -i sample-registry/sample-policy-signature:0.0.1
You can confirm the YAML content is signed with the presence of the cosign.sigstore.dev/imageRef annotation as shown below:
If you would like to use a signature in the private OCI registry for manifest verification, you need to create a secret to provide Docker credentials to Integrity Shield. Follow this README_OCI_REGISTRY to enable signature verification with a private OCI registry.
- Enable enforce mode. We have confirmed that all policies on the cluster are valid now, so we are ready to switch from
informtoenforcemode. To switch the mode, only one simple step is required. You need to change theaction.modefield in the policy-constraint included in policy-integrity-shield policy. See the following image:
Once the change has been applied, K8s Integrity Shield blocks any policy creation and change request without a signature. In enforce mode, Integrity Shield generates Event resources to report that invalid requests occurred within the cluster. The policy-integrity-shield-events policy is used for checking the existence of this kind of Integrity Shield Event. You can see whether there are any violations from the policy-integrity-shield-events policy status in the web console.
In order to update the policy, you will need to sign the updated policy again, following the same procedure as in step 3. Throughout this blog, I have described how you can use the new features of Integrity Shield to protect policies for Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes. In this way, you can ensure the integrity of policies based on signature.
저자 소개
채널별 검색
오토메이션
기술, 팀, 인프라를 위한 IT 자동화 최신 동향
인공지능
고객이 어디서나 AI 워크로드를 실행할 수 있도록 지원하는 플랫폼 업데이트
오픈 하이브리드 클라우드
하이브리드 클라우드로 더욱 유연한 미래를 구축하는 방법을 알아보세요
보안
환경과 기술 전반에 걸쳐 리스크를 감소하는 방법에 대한 최신 정보
엣지 컴퓨팅
엣지에서의 운영을 단순화하는 플랫폼 업데이트
인프라
세계적으로 인정받은 기업용 Linux 플랫폼에 대한 최신 정보
애플리케이션
복잡한 애플리케이션에 대한 솔루션 더 보기
오리지널 쇼
엔터프라이즈 기술 분야의 제작자와 리더가 전하는 흥미로운 스토리
제품
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux
- Red Hat OpenShift Enterprise
- Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform
- 클라우드 서비스
- 모든 제품 보기
툴
체험, 구매 & 영업
커뮤니케이션
Red Hat 소개
Red Hat은 Linux, 클라우드, 컨테이너, 쿠버네티스 등을 포함한 글로벌 엔터프라이즈 오픈소스 솔루션 공급업체입니다. Red Hat은 코어 데이터센터에서 네트워크 엣지에 이르기까지 다양한 플랫폼과 환경에서 기업의 업무 편의성을 높여 주는 강화된 기능의 솔루션을 제공합니다.