Part 2: LDAP Authentication in OpenShift using Red Hat Identity Manager (RH IDM)
In this part, we will introduce the authentication mechanism using LDAP among the multiple ways of authenticating on the OpenShift Container Platform (OCP). OCP is the leading hybrid cloud enterprise Kubernetes application platform. Part 1 of this blog, authentication to OCP using OpenID connect can be found in the references section.
OCP supports a number of Identity Providers (IdP) using OAuth configuration to allow users to log in to the platform.
This figure represents the broad spectrum of IdP choices supported by OCP at this time.

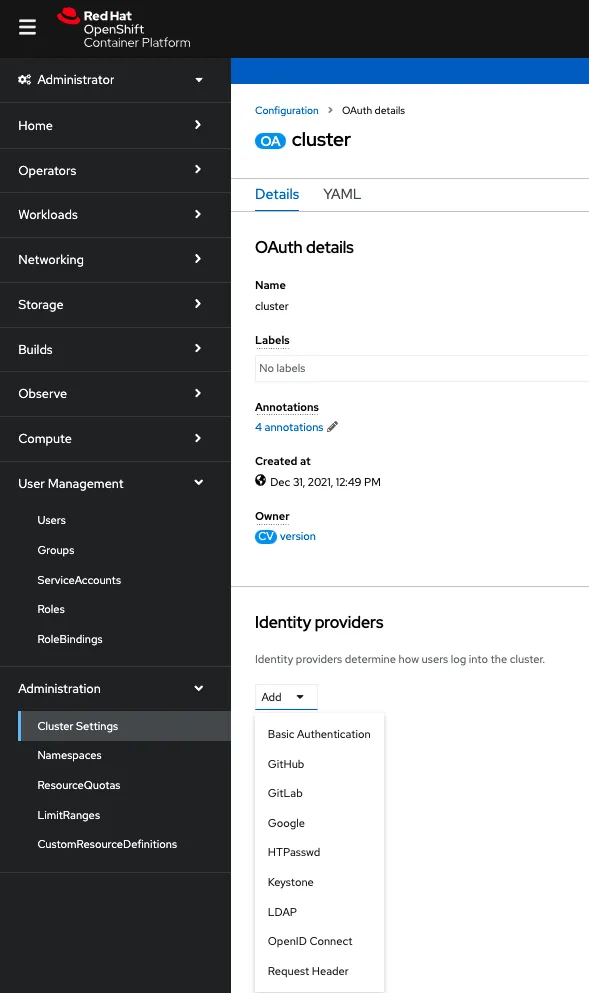
When there is no IdP configured, only one can be added through the User Management option in the console by clicking Add IdP or one or more any time from the cluster settings options as shown below. Typically cluster admin level access or roles with IdP capabilities can configure these options.
Note: Multiple IdP's can co-exist to authenticate in to a OpenShift Cluster.
This repository can help bootstrap the different Identity Providers that OpenShift can authenticate with. You'll find documentation for each specific IdP mechanism and automation to drive the deployments.
LDAP Authentication
We will demonstrate the LDAP authentication using a Red Hat Identity Manager (RH IDM) server that we created.
Red Hat Identity Manager(RHPDM) provides many feature including:
- Maintain the identities and grouping mechanisms in one central place: the IdM server
- Centrally manage different types of credentials such as passwords, PKI certificates, OTP tokens, or SSH keys
- Apply policies uniformly to multiples of machines at the same time
- Manage POSIX and other attributes for external Active Directory users
- Set different access levels for users by using host-based access control, delegation, and other rules
- Centrally manage privilege escalation rules (sudo) and mandatory access control (SELinux user mapping)
- Maintain central PKI infrastructure and secrets store
To set up RHIDM Server follow the instructions in the Prerequisites section below
To set up RH IDM as the LDAP Server for OCP, follow the steps outlined here - https://github.com/kenmoini/openshift-identity-crisis/tree/main/ldap
Once the RH IDM server is set up, follow these steps to download the CA certificate. You will need it later while integrating with OCP.
- Click on the Authentication tab. A list of certificates will be displayed.
- Click on the Serial Number 1 link for the CA Certificate.
- Click on the ‘Actions’ menu and select ‘Download’.

To integrate OCP with the LDAP Server, you can either use the OCP web console or use the 'oc' commands. We will go over both options below.
Option 1: Using OCP Web Console
- Log into the OCP console using cluster admin privileges.
- Switch to the Administrator perspective, if not already on it.
- Navigate to Cluster Settings under the Administration menu on the left.
- Click on the Configuration tab on the right, and search for the text ‘OAuth’.
- Select OAuth and scroll to the bottom of the page. You will see the Identity Providers that are present.
- Click on the Add dropdown and select LDAP. A form will appear.
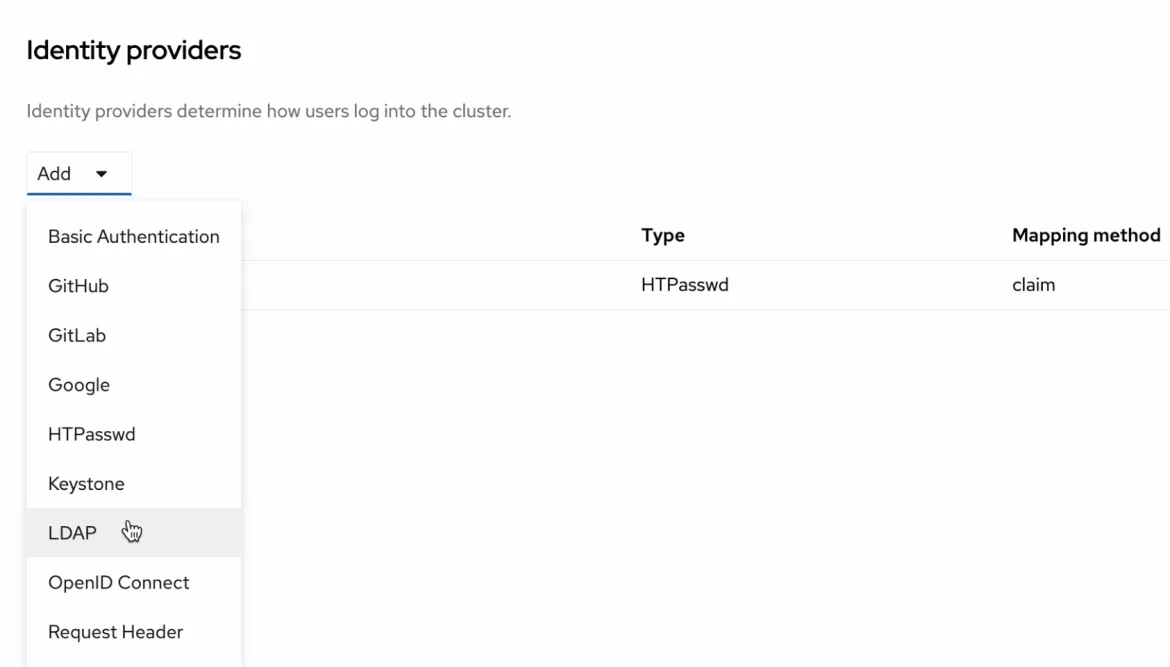
7. Enter the following details:
-
- Name: You can use any name of your choice.
- URL: A URL in RFC2255 format. In our case, with RHIDM, it looks something like this - ldaps://:636/cn=users,cn=accounts,dc=7zh7k,dc=sandbox2966,dc=opentlc,dc=com?uid?sub?(uid=*)
- Bind DN: This has the UID of the LDAP Admin user, followed by the common names and domain components. In our case, uid=admin,cn=users,cn=accounts,dc=5ea8,dc=sandbox1013,dc=opentlc,dc=com
- Bind password: Password of the LDAP Admin user. In our case, s3cur3P455W0rd
-

Attributes: Most of this is already mapped. You can add 'mail' to map the 'email' field.

-
- CA file: Add the CA Certificate file downloaded from the LDAP Server. The steps for downloading the certificate from RH IDM are given above.
- 9. Create a config map for the CA certificate.
- 10. This configuration can be added manually to the configuration YAML or through the automated configure.sh from the ldap folder on the github project.
Option 2: Using ‘oc’ commands
- Create a secret for the Bind Password called ldap-bind-password. If you used our script, it is the admin password, otherwise use the password from your LDAP with admin access.
export BIND_PASSWORD="s3cur3P455W0rd"
oc create secret generic ldap-bind-password --from-literal=bindPassword=${BIND_PASSWORD} -n openshift-config
Note: The secret key must be called as bindPassword as you see above.
- Create a config map for the CA certificate.
oc create configmap ldap-ca-cert --from-file=ca.crt=<cert-file-name>.pem -n openshift-config
Note: The config map key must be called ca.crt
- This configuration can be added manually to the configuration YAML or through the automated configure.sh from the ldap folder on the github project.

apiVersion: config.openshift.io/v1
kind: OAuth
metadata:...
spec:
identityProviders:
- htpasswd:...
- ldap:
attributes:
email:
id:
- dn
name:
- cn
preferredUsername:
- uid
bindDN: >-
uid=admin,cn=users,cn=accounts,dc=7zh7k,dc=sandbox2966,dc=opentlc,dc=com
bindPassword:
name: ldap-bind-password-bz8mz
ca:
name: ldap-ca-pnhsg
insecure: false
url: >-
ldaps://idm.7zh7k.sandbox2966.opentlc.com:636/cn=users,cn=accounts,dc=7zh7k,dc=sandbox2966,dc=opentlc,dc=com?uid?sub?(uid=*)
mappingMethod: claim
name: ldap-auth
type: LDAP
- You can now log out to test the LDAP integration.
You can now see ldap-auth as an additional IdP option on the login screen. You can use it to log in using your LDAP credentials.

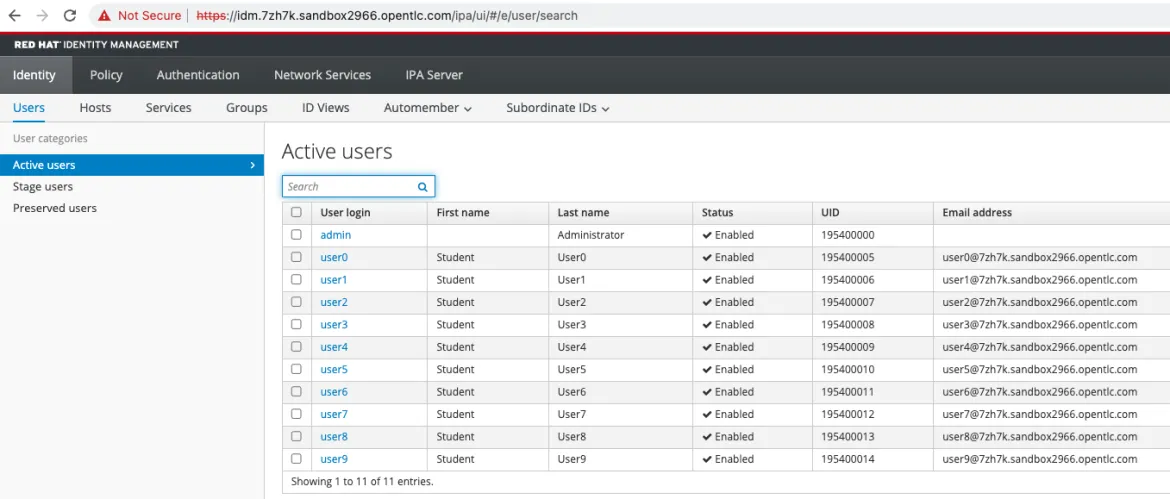
Based on the RHIDM server set up below in this example user names can be admin with password or any of the users user1, user2…user9 can be used.
Prerequisite - Setting up Red Hat Identity Manager(RHIDM):
You can use this Ansible playbook to create an RHIDM server on AWS among other things such as bastion server, OpenShift Container Platform(OCP) cluster, Gitlab server etc.., By configuring variables files this can be accomplished quickly standing up RHIDM server in AWS on an ec2 instance that will be created by the Ansible script. Detailed instructions and the required code can be found in this repo, while we explain some high level steps below.
https://github.com/kenmoini/grain-tower
You'll need an SSH Key Pair - if you don't already have one, create a set via the following command:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -f ~/.ssh/idprsa
The Private Key is secret and will be used to actually connect to created VMs, the Public Key will be passed along to the Playbooks and to AWS to create AWS EC2 Keys from.
If the ssh-agent process is not already running for your local user, start it as a background task:
eval $(ssh-agent -s)
Add your SSH private key to the ssh-agent:
ssh-add ~/.ssh/idprsa
git clone https://github.com/kenmoini/grain-tower
Ensure you have got the aws_access_key_id, aws_secret_access_key and region fields associated to the AWS account where the IDM server will be created. Also locally execute the aws configure command to input these values.
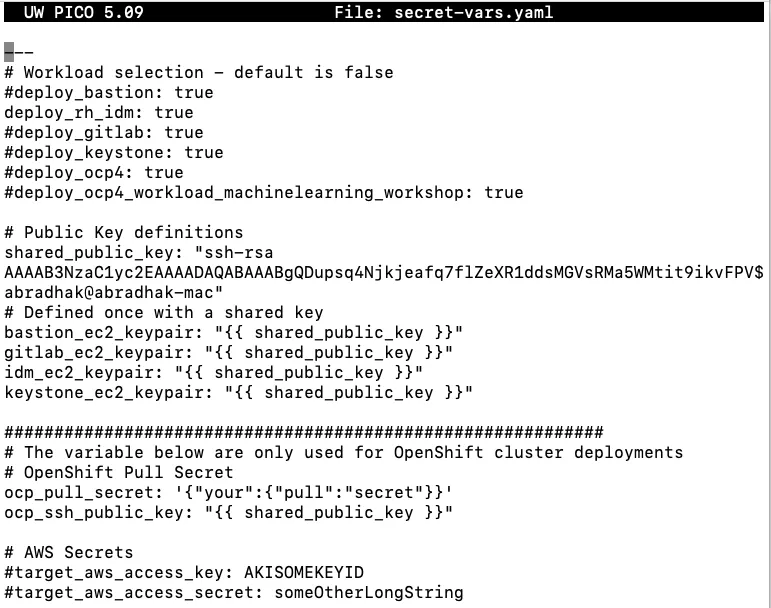
With your AWS keys in place and an SSH Key Pair at hand, you can create a file called secret-vars.yaml where you can include variable overrides - see example.secret-vars.yaml for standard variables used.
cp example.secret-vars.yaml secret-vars.yaml
Modify secret-vars.yaml , since we want to stand up only IDM server the deploy_rh_idm: true is not commented
deploy_rh_idm: true
Public Key definitions
shared_public_key: ”replace with the contents of idprsa.pub key in ~/.ssh/idprsa.pub key” AWS access key and secret key can be passed as an environment variable so can be commented in the file.
Execute the ansible-playbook command using the secret-vars.yaml file and
ansible-playbook -e "@secret-vars.yaml" -e target_aws_access_key=${AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID} -e target_aws_access_secret=${AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY} bootstrap.yamlWhen this ansible script completes successfully it will display the idm URL link a few times and it is typically of the pattern idm.domainname.
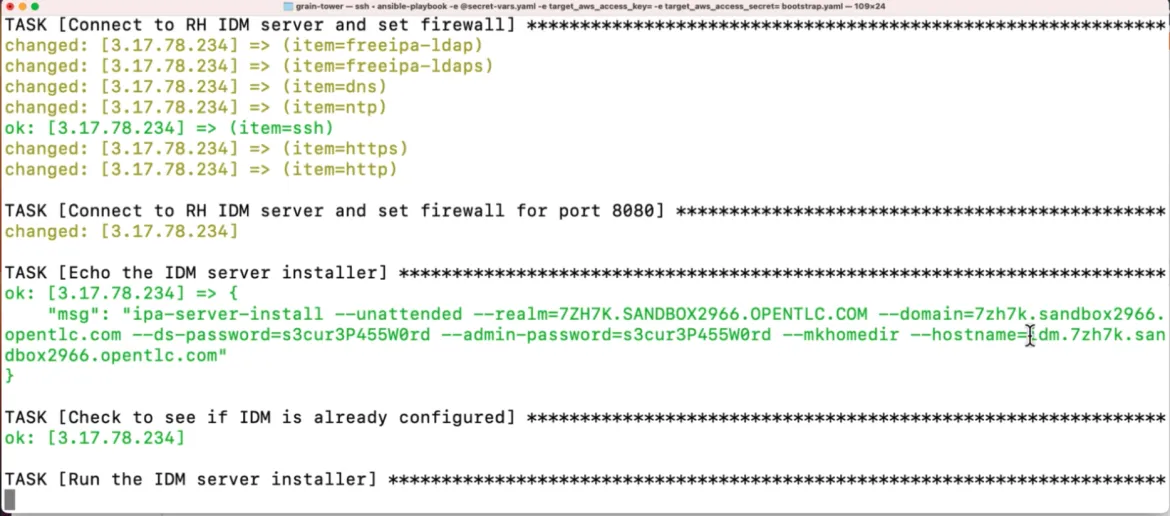
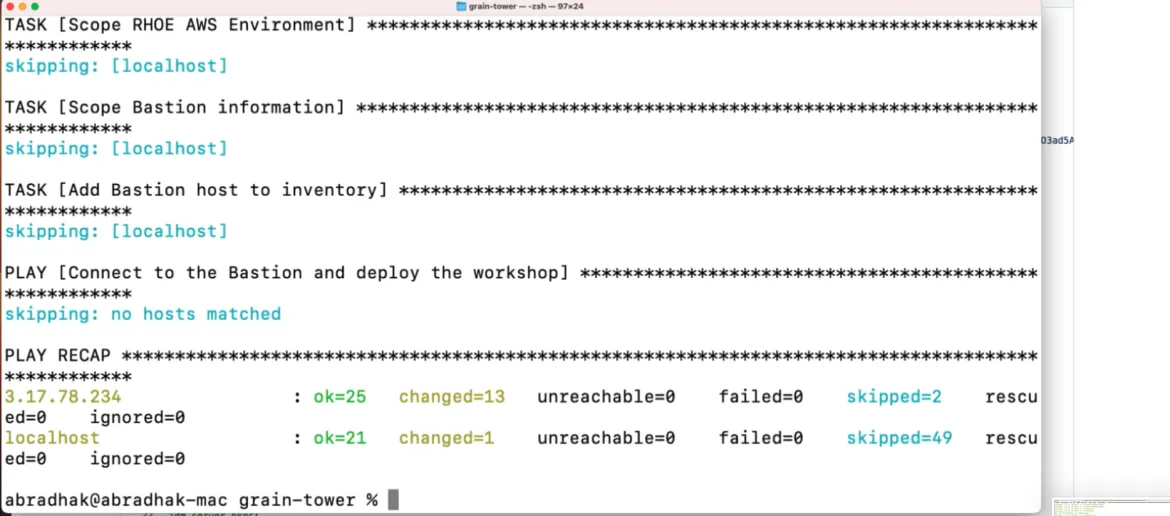
Occasionally the script can fail due to some timeout reasons completing only the partial steps, then you can simply re-execute the command and with the immutable nature it will not duplicate the steps that are successfully completed and finish the process.
Displays the RHIDM console with users admin and 10 other users from user0,1…9
Conclusion
OpenShift directly supports many ways for users to log in to the cluster. We covered the LDAP IdP provider in this blog using Red Hat Identity Manager as the LDAP server. But any LDAP compliant servers like Active Directory can be integrated using this approach,
References:
- LDAP provider for openshift - https://github.com/kenmoini/grain-tower/tree/main/rh-idm-on-rhoe-aws
- Ansible scripts to install bastion, OpenShift, SSO, IDM, private Gitlab, Keystone - https://github.com/kenmoini/grain-tower
- Scripts for all the IdPs - https://github.com/kenmoini/openshift-identity-crisis
- Redhat detailed references - https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/4.11/authentication/identity_providers/configuring-github-identity-provider.html
- https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/4.11/authentication/understanding-identity-provider.html
- Authentication methods in Openshift: Part-1 - OpenID Connect Authentication in to OpenShift using Red Hat Single Sign-On
- Video - https://youtu.be/HM6nhNESCi8
- OpenShift Container Platform(OCP) Authentication IdP using LDAP with Red Hat Identity Manager(RHIDM)
- Video - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x51vFcUw6V8
- Subscribe to SE Synergy and Acceleration channel - https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCqMv_XDUDenRYi26UElraeg
product trial
Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform | 제품 체험판
저자 소개
Abay Radhakrishnan has more than 30 years of experience in the consulting, IT and software fields with focus on emerging technologies. He plays a unique combination of an enterprise architect and cloud strategy and solutions architect. As a technical management personnel, he has deep experience in defining, architecting, managing and implementing large-scale enterprise architectures and solutions.
유사한 검색 결과
Red Hat blog
OpenShift blog
Stay updated on all things Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) at Red Hat.
채널별 검색
오토메이션
기술, 팀, 인프라를 위한 IT 자동화 최신 동향
인공지능
고객이 어디서나 AI 워크로드를 실행할 수 있도록 지원하는 플랫폼 업데이트
오픈 하이브리드 클라우드
하이브리드 클라우드로 더욱 유연한 미래를 구축하는 방법을 알아보세요
보안
환경과 기술 전반에 걸쳐 리스크를 감소하는 방법에 대한 최신 정보
엣지 컴퓨팅
엣지에서의 운영을 단순화하는 플랫폼 업데이트
인프라
세계적으로 인정받은 기업용 Linux 플랫폼에 대한 최신 정보
애플리케이션
복잡한 애플리케이션에 대한 솔루션 더 보기
오리지널 쇼
엔터프라이즈 기술 분야의 제작자와 리더가 전하는 흥미로운 스토리
제품
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux
- Red Hat OpenShift Enterprise
- Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform
- 클라우드 서비스
- 모든 제품 보기
툴
체험, 구매 & 영업
커뮤니케이션
Red Hat 소개
Red Hat은 Linux, 클라우드, 컨테이너, 쿠버네티스 등을 포함한 글로벌 엔터프라이즈 오픈소스 솔루션 공급업체입니다. Red Hat은 코어 데이터센터에서 네트워크 엣지에 이르기까지 다양한 플랫폼과 환경에서 기업의 업무 편의성을 높여 주는 강화된 기능의 솔루션을 제공합니다.


