One of the new features we added in Red Hat Ansible Tower 3.2 was support for custom credentials. The idea of custom credentials is pretty simple. In addition to the built-in credentials supported by Ansible Tower such as SSH keys, username/password combos, or cloud provider credentials, we now let the user define their own credentials for storing securely in Ansible Tower and exposing to playbooks.
However, this simplicity belies real power, opening up many new ways to automate. Let's dive into the details.
HOW CUSTOM CREDENTIALS WORK
To set up a custom credential, first you must define the custom credential Type.
Credential types consist of two key concepts - "inputs" and "injectors".
Inputs define the value types that are used for this credential - such as a username, a password, a token, or any other identifier that's part of the credential.
Injectors describe how these credentials are exposed for Ansible to use - this can be Ansible extra variables, environment variables, or templated file content.
Once you've defined a new Credential Type, you can then create any number of credentials that use that type. We'll go through examples to shed light on how this can be used to automate easier and in more ways.
CUSTOM CREDENTIALS - A SIMPLE EXAMPLE
We will start with a simple task - registering your Red Hat Enterprise Linux machines.
Even if you're opening up provisioning to your whole organization, you want to
make sure they're on the right account so they can be properly managed and tracked...
without necessarily exposing the password to your users.
To do this, we'll create a new Custom Credential type - Red Hat Subscription Manager.
Let's dig in more on the "input" and "injector" settings. Both the input and injector
definitions can be provided in either JSON or YAML format. We'll use YAML here for readability.
This Red Hat Subscription Manager consists of a username and password. We'll define the
inputs like this:
fields:
- type: string
id: username
label: Subscription manager username
- type: string
id: password
label: "Subscription manager password (🙈🙉🙊)"
secret: True
required:
- username
- password
This creates a credential with two keys: username and password. Note the secret: True flag on the password key - this means it's a secret that should be stored encrypted in the Ansible Tower database. We mark both keys as required, since you need them both.
Now how should we expose this to playbooks? The redhat_subscription module takes username and password as parameters, so the simplest way to do this is to pass them as extra variables. Hence, our injector looks like this:
extra_vars:
rhsm_password: '{{ password }}'
rhsm_username: '{{ username }}'
This passes the username and password for this credential via the extra variables rhsm_username and rhsm_password.
We can now create a credential that uses this type.

Now, we can write playbooks to use credentials of this type. Here's a short playbook example.
---
- hosts: all
gather_facts: True
tasks:
- name: Install RHSM and Insights
yum:
name: '{{ item }}'
state: present
with_items:
- redhat-access-insights
- subscription-manager
- name: Register system
redhat_subscription:
state: present
username: '{{ rhsm_username }}'
password: '{{ rhsm_password }}'
ANOTHER EXAMPLE - USING THIRD-PARTY CREDENTIAL STORAGE
A common usage pattern in large enterprises is the use of a third-party credential management system for managing passwords and keys for accessing hosts and services.
Before, this sort of environment was tricky to manage with Ansible and Ansible Tower. Now, with the combination of Ansible Tower Custom Credentials + Ansible Lookup Plugins, it becomes simple.
Here's an example using HashiCorp Vault. Other credential storage systems would follow a similar pattern.
First, we need a Hashi Vault credential type. There are two main parameters used to configure the connection to Hashi Vault - the URL to the vault itself, and a token to use. These are used by the lookup plugin via the environment variables VAULT_ADDR and VAULT_TOKEN.
That would make our credential input and injector definitions look like this:
fields:
- type: string
id: vault_server
label: URL to Vault Server
- type: string
id: vault_token
label: Vault Token
secret: true
required:
- vault_server
- vault_tokenenv:
VAULT_ADDR: '{{ vault_server }}'
VAULT_TOKEN: '{{ vault_token }}'
Given these, let's create our new credential.
To use this in our playbook, all we need is to mark that our hosts will actually get their connection information from vault.
We'll do that in inventory.
Here's a test playbook that demonstrates how we're connecting.
---
- hosts: all
gather_facts: true
tasks:
- name: "What's my name again?"
debug:
msg: '{{ ansible_user }}'
Now, let's run our playbook!
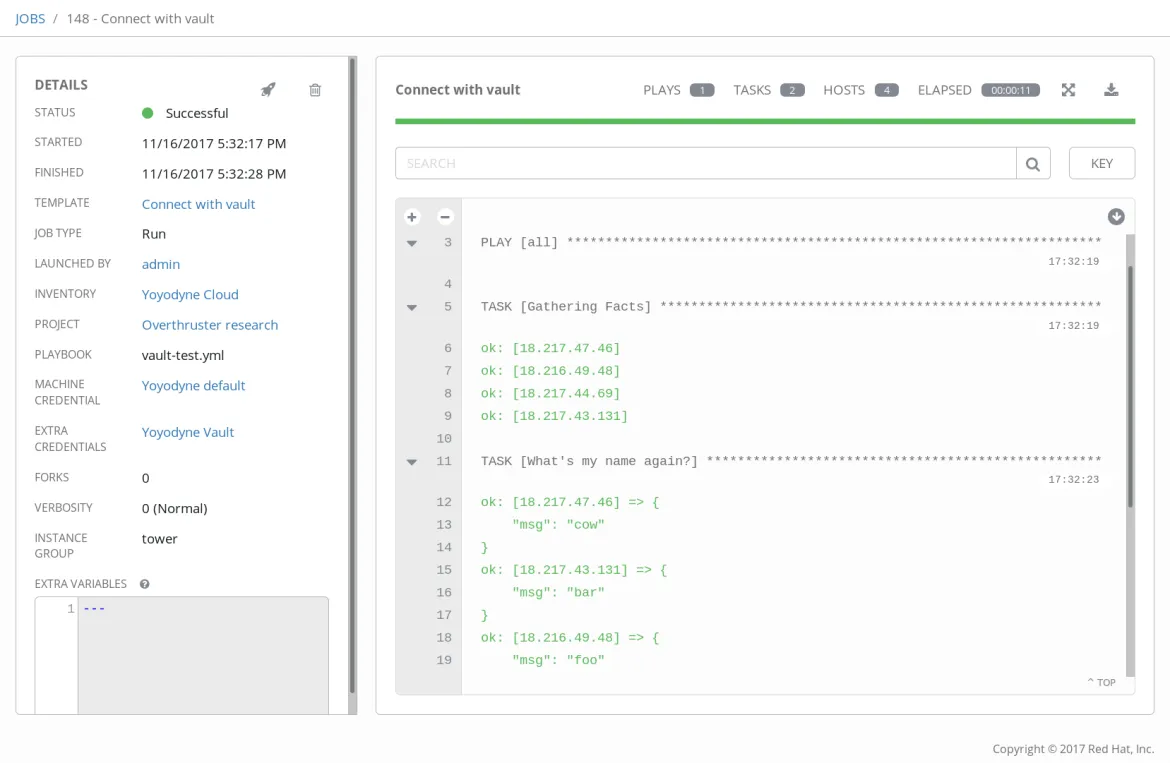
With this, we're using our single vault token to look up the appropriate password to connect to the managed hosts from our password vault, without ever knowing what the password might be. It could even be rotated every few weeks, and we'd never have to change our automation.
WRAP UP
We hope that this helps explains just how the new custom credential feature in Ansible Tower 3.2 can be used to allow you to automate more things in more ways.For more information on custom credentials, please see the Ansible Tower documentation
To get started with Ansible Tower, go to https://www.ansible.com/tower-trial
Sobre o autor
Navegue por canal
Automação
Últimas novidades em automação de TI para empresas de tecnologia, equipes e ambientes
Inteligência artificial
Descubra as atualizações nas plataformas que proporcionam aos clientes executar suas cargas de trabalho de IA em qualquer ambiente
Nuvem híbrida aberta
Veja como construímos um futuro mais flexível com a nuvem híbrida
Segurança
Veja as últimas novidades sobre como reduzimos riscos em ambientes e tecnologias
Edge computing
Saiba quais são as atualizações nas plataformas que simplificam as operações na borda
Infraestrutura
Saiba o que há de mais recente na plataforma Linux empresarial líder mundial
Aplicações
Conheça nossas soluções desenvolvidas para ajudar você a superar os desafios mais complexos de aplicações
Programas originais
Veja as histórias divertidas de criadores e líderes em tecnologia empresarial
Produtos
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux
- Red Hat OpenShift
- Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform
- Red Hat Cloud Services
- Veja todos os produtos
Ferramentas
- Treinamento e certificação
- Minha conta
- Suporte ao cliente
- Recursos para desenvolvedores
- Encontre um parceiro
- Red Hat Ecosystem Catalog
- Calculadora de valor Red Hat
- Documentação
Experimente, compre, venda
Comunicação
- Contate o setor de vendas
- Fale com o Atendimento ao Cliente
- Contate o setor de treinamento
- Redes sociais
Sobre a Red Hat
A Red Hat é a líder mundial em soluções empresariais open source como Linux, nuvem, containers e Kubernetes. Fornecemos soluções robustas que facilitam o trabalho em diversas plataformas e ambientes, do datacenter principal até a borda da rede.
Selecione um idioma
Red Hat legal and privacy links
- Sobre a Red Hat
- Oportunidades de emprego
- Eventos
- Escritórios
- Fale com a Red Hat
- Blog da Red Hat
- Diversidade, equidade e inclusão
- Cool Stuff Store
- Red Hat Summit





