Training a large language model (LLM) probably sounds like a specialized and highly technical task. Until recently, that was true, but the InstructLab project has been putting in the work required to make it easier for anyone to train an LLM. That means you can contribute to the development of artificial intelligence (AI), either because your organization needs domain-specific knowledge for its AI solution, or just because you want to help improve open source AI. All you need to know is how to type text in a simple format called YAML, and this article is going to teach you exactly how to do that.
Open a text editor
An LLM establishes probable responses to questions by analyzing existing content about a specific topic. The easiest way to contribute to an LLM is to contribute knowledge about a topic, in the form of questions and answers. All you need for that is a text editor.
A text editor is like a simplified word processor. There are lots of them out there, including Notepad++ and Notepadqq, Pulsar and VSCodium , so just choose the one that works for you.
Download the template
The InstructLab provides a template file for knowledge content so you don’t have to start from a blank file. To download the template, open a web browser to github.com/instructlab/taxonomy and then click the green Code button in the top right corner and select Download ZIP.
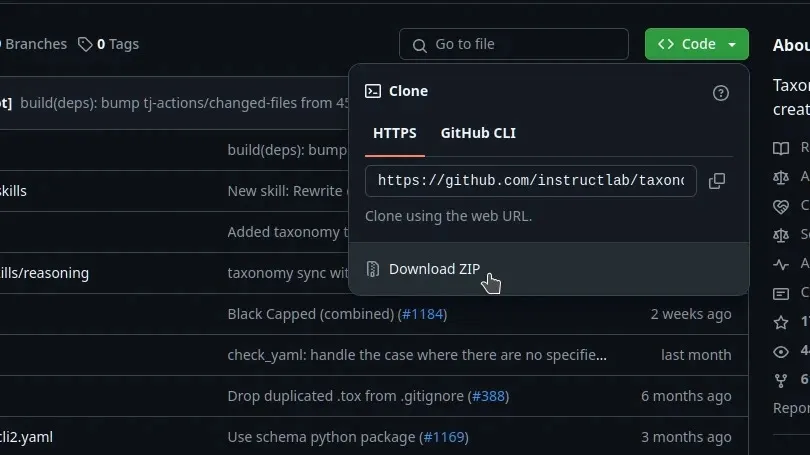
Once the files have downloaded, find the ZIP archive in your Downloads folder and unzip it. This produces a new folder called taxonomy.
Write simplified YAML
In the docs folder within the taxonomy directory, open the file named template_qna.yaml in your text editor. This file contains a blank question-and-answer session you can use as a template for the knowledge you want to provide training for.
YAML is designed to be simple, but the amount of YAML you need for this is even simpler. Mostly, YAML is a collection of labels (also called a “key” or “mapping”) and descriptions (also called a “value”), which is how a lot of data on the internet is structured. When you go to your favorite online store, you probably shop by clicking on a label (the name of an item) and then you read its description. When you write a report for work or school, you probably write a subheading, and then you write a paragraph explaining more about that subheading. InstructLab’s use of YAML is based on the exact same concept.
Here’s an abbreviated sample of the blank YAML template:
version: 3
domain: <The knowledge domain>
created_by: <Your name>
seed_examples:
- context: |
<Context from the document associated with this set of sample q&a pairs.>
questions_and_answers:
- question: |
<A relevant question used for synthetic data generation.>
answer: |
<The desired response for the question.> The data at the top of the document establishes the knowledge domain you’re writing about, and who you are. If you’re contributing to the InstructLab project, then you must use your GitHub user name as the description of the created_by label. If you’re contributing to a private LLM, then you can use your name or whatever description the project manager has requested.
The seed_examples is the main label for the knowledge section you’re about to create. It doesn’t require a description, because it contains yet more labels.
The context label is essentially a subheading, and it requires a statement from you that describes the kind of conversation that might lead to the questions and answers you’re about to enter. For example, to add a question and answer session about some aspect of the ancient Ptolemaic empire, you might describe its context as “The kings and queens of the Ptolemaic empire.” To enter questions and answers about the works of Edgar Rice Burroughs, you might write “The literature of Edgar Rice Burroughs.” Just imagine you’re writing a report for school. It’s the same logic.
Indentation is important
YAML is a sequence of label after label, so it relies on indentation to represent the flow of logic. In a word processor, a heading is often displayed as large and bold text compared to the text in a paragraph. Instead of using font size and style, YAML uses indentation.
When you write a description in InstructLab’s YAML file, you write it on the line under the label, and you add two spaces to the level of indentation. This is how the template is structured, so it’s a pretty easy pattern to fall into.
Questions and answers
Next is the actual question and answer section. Under each question heading, you write exactly one question that you might anticipate in a conversation about your chosen topic. Under each answer heading, you write a simple answer to that question.
It’s best to keep both the questions and answers short and concise, because that ensures that they’re modular and distinct. Don’t try to sneak two questions into one, especially when the answer to one question has no bearing on the answer to the second. It’s misleading to ask “Did Edgar Rice Burroughs write the Tarzan book and movie?” as one question, because Edgar Rice Burroughs wrote the Tarzan books whether or not he wrote a Tarzan screenplay.
Write a distinct question and a focused answer so that the LLM can use your knowledge to extrapolate correct data. Here’s an example:
version: 3
domain: Ptolemaic empire
created_by: Tux
seed_examples:
- context: |
Discussion of Cleopatra.
questions_and_answers:
- question: |
How many Ptolemaic queens were named Cleopatra?
- answer: |
There were 7 Ptolemaic queens named Cleopatra. YAML for InstructLab
YAML is a way of writing text so that it has predictable structure, which makes it easy for computers to process. Follow the InstructLab template, add your knowledge to the LLM of your choice, and help improve AI. If you need reinforcement for what you’ve learned from this article, check out this video introduction on how to get started!
Sobre el autor
Seth Kenlon is a Linux geek, open source enthusiast, free culture advocate, and tabletop gamer. Between gigs in the film industry and the tech industry (not necessarily exclusive of one another), he likes to design games and hack on code (also not necessarily exclusive of one another).
Más similar
Navegar por canal
Automatización
Las últimas novedades en la automatización de la TI para los equipos, la tecnología y los entornos
Inteligencia artificial
Descubra las actualizaciones en las plataformas que permiten a los clientes ejecutar cargas de trabajo de inteligecia artificial en cualquier lugar
Nube híbrida abierta
Vea como construimos un futuro flexible con la nube híbrida
Seguridad
Vea las últimas novedades sobre cómo reducimos los riesgos en entornos y tecnologías
Edge computing
Conozca las actualizaciones en las plataformas que simplifican las operaciones en el edge
Infraestructura
Vea las últimas novedades sobre la plataforma Linux empresarial líder en el mundo
Aplicaciones
Conozca nuestras soluciones para abordar los desafíos más complejos de las aplicaciones
Programas originales
Vea historias divertidas de creadores y líderes en tecnología empresarial
Productos
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux
- Red Hat OpenShift
- Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform
- Servicios de nube
- Ver todos los productos
Herramientas
- Training y Certificación
- Mi cuenta
- Soporte al cliente
- Recursos para desarrolladores
- Busque un partner
- Red Hat Ecosystem Catalog
- Calculador de valor Red Hat
- Documentación
Realice pruebas, compras y ventas
Comunicarse
- Comuníquese con la oficina de ventas
- Comuníquese con el servicio al cliente
- Comuníquese con Red Hat Training
- Redes sociales
Acerca de Red Hat
Somos el proveedor líder a nivel mundial de soluciones empresariales de código abierto, incluyendo Linux, cloud, contenedores y Kubernetes. Ofrecemos soluciones reforzadas, las cuales permiten que las empresas trabajen en distintas plataformas y entornos con facilidad, desde el centro de datos principal hasta el extremo de la red.
Seleccionar idioma
Red Hat legal and privacy links
- Acerca de Red Hat
- Oportunidades de empleo
- Eventos
- Sedes
- Póngase en contacto con Red Hat
- Blog de Red Hat
- Diversidad, igualdad e inclusión
- Cool Stuff Store
- Red Hat Summit

