In the context of supply chain optimization, intelligent order refers to the use of advanced algorithms and techniques to determine the optimal order quantity, timing and placement for each product within the supply chain network. This involves analyzing various factors—such as demand patterns, lead times, production and transportation costs, inventory levels and customer service levels—to make data-driven decisions that maximize efficiency and profitability.
Overall, intelligent order management is an essential component of supply chain optimization, as it enables businesses to better manage their inventory and respond to changing market conditions in a timely and efficient manner.
Intelligent order management systems can help businesses reduce excess inventory, avoid stockouts, improve delivery times and enhance overall supply chain performance. By leveraging real-time data and predictive analytics, these systems can automatically adjust inventory levels and reorder points, allocate inventory across multiple locations and optimize transportation routes to minimize costs and reduce delivery times.
One particular aspect of intelligent order that we are focused on in this article is using inventory management systems and machine learning (ML)/artificial intelligence (AI) to provide effective last mile delivery.
Last mile delivery, also known as last mile logistics, refers to the final leg of the delivery process, where goods are transported from a local hub or distribution center to the customer's doorstep or preferred delivery location. It is the most crucial and expensive part of the delivery process, as it typically involves the use of smaller vehicles to navigate through crowded urban areas and deliver goods to individual customers.
Last mile delivery is often considered a primary bottleneck of the supply chain, as it involves complex logistical challenges such as traffic congestion, unpredictable delivery locations, and varying customer demands (e.g., installation of large or bulky items). Yet, it remains a critical area of focus for businesses seeking to optimize their supply chain operations and meet the evolving demands of today's consumers, especially in light of the increase in deliveries direct to consumers. It can be a tricky balancing act between meeting consumer and business expectations and optimizing for low delivery costs.
Solution overview
The diagram below provides a high-level overview of the intelligent order solution including the core application systems, the foundational infrastructure built on Red Hat OpenShift, and the inventory optimization platform.
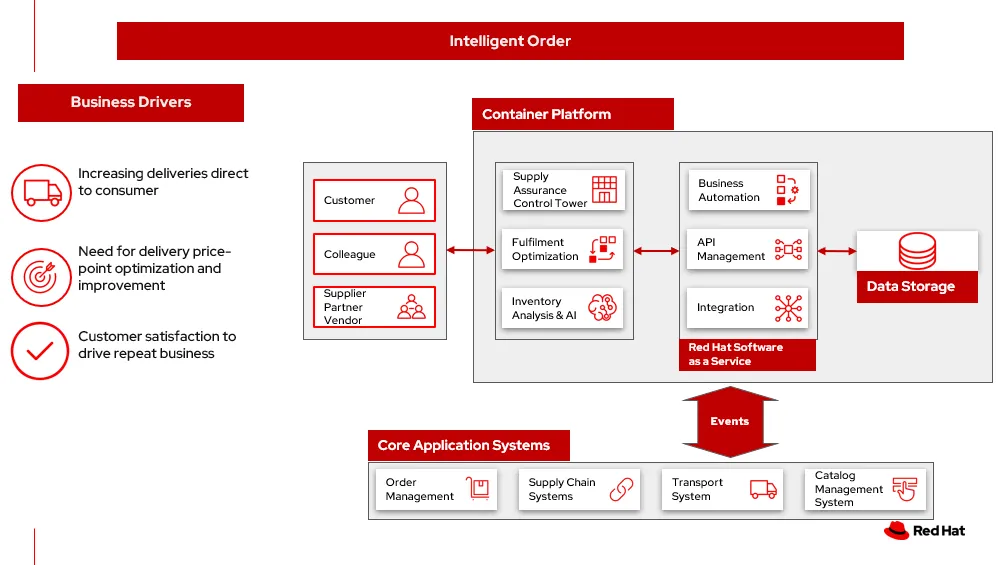
An important point to recognize with intelligent order is that, as with a variety of other supply chain optimization techniques, benefits accrue to both the business and the consumer from having data-driven inventory management. When all goes as planned, the company gets lower costs and a more resilient system, and the customer gets a more predictable and better delivery experience. It’s a win for both parties.
Architecture
The following diagram shows the workflow of an intelligent order use case.
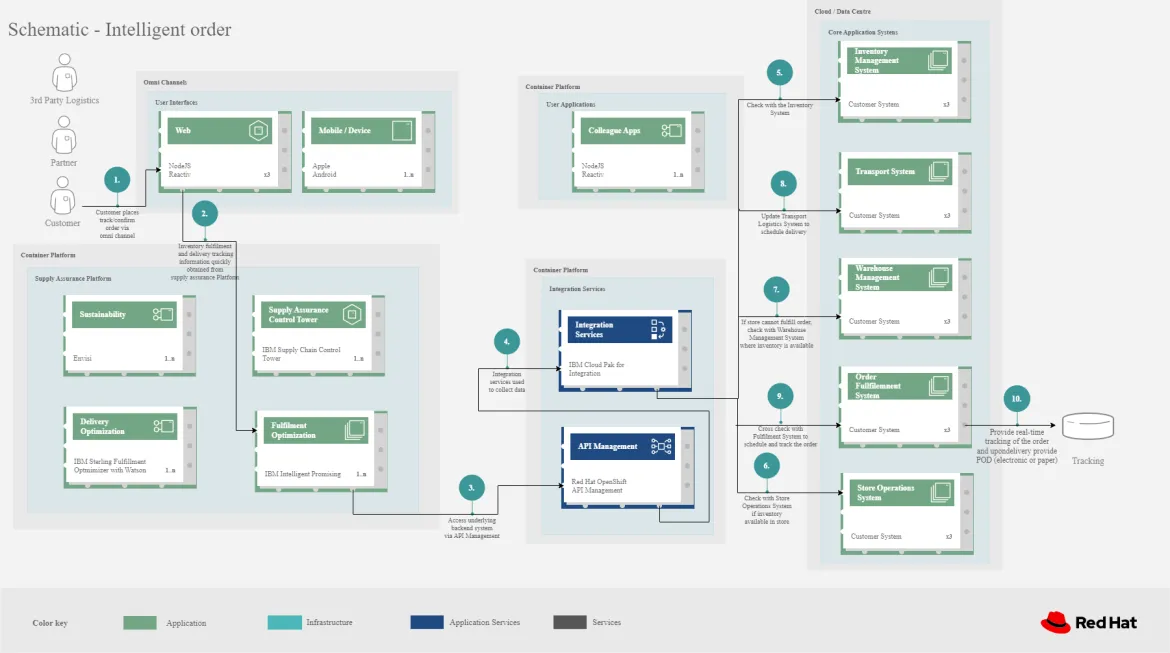
The steps in that workflow are as follows.
It begins with a customer placing or otherwise interacting with an order through the omni-channel. Omni-channel refers to the integration of all channels and touchpoints that a retailer uses to interact with its customers, whether it is in-store, online, through mobile devices, social media or any other means.
After the order is placed, inventory fulfillment and delivery tracking information is delivered from the supply assurance platform; the backend systems are accessed via API Management and Integration Services. The Inventory Management System checks with the Store Operations System to see if the inventory is available in the store. If the store cannot fulfill order, the system then checks with the Warehouse Management System to see where inventory is available.
Once the ordered items are found, the Transport/Logistics System is updated to schedule delivery, then the Fulfillment System is cross-checked to schedule and track the order. Real-time tracking of the order is maintained throughout the process and proof-of-delivery (electronic or paper) is provided upon delivery.
Action Guide
From a high-level perspective, there are several main steps your organization can take to drive innovation and move toward a digital supply chain. For specific steps on this approach, see The Action Guide details in Own your transformation survey of 1500 CSCOs across 24 industries. It covers actionable steps in several areas of automation, sustainability, as well as the modernization to hybrid cloud platforms.
Summary
Intelligent order refers to the use of advanced algorithms and techniques to determine the optimal order quantity, timing and placement for each product within the supply chain network. In this article, we’ve specifically discussed using intelligent order approaches to drive improved customer satisfaction with respect to last mile delivery.
If you are interested in more solutions built with these and other products in Red Hat's portfolio visit the Portfolio Architecture website and the Intelligent Order Portfolio Architecture, in particular.
Supply Chain blog series
This blog is part of a Supply Chain blog series:
- Supply chain optimization imperative – Read the blog
- Supply chain optimization – See the blog and associated Portfolio Architecture
- Demand risk – See the blog and associated Portfolio Architecture
- Loss and waste management – See the blog and associated Portfolio Architecture
- Product timeliness – See the blog and associated Portfolio Architecture
- Perfect order – See the blog and associated Portfolio Architecture
- Intelligent order – this blog and associated Portfolio Architecture
- Sustainable supply (coming soon)
執筆者紹介
Bruce joined IBM as a Solutions Architect focusing on distribution and communication sectors in the industry market in 2021 in Client Engineering. Bruce has been a solutions architect since 2001. He led the initial cloud migrations to Microsoft Azure, managed research compute resources at Microsoft Research and built out Kubernetes implementations.
Karl joined Red Hat in 2021 as a Chief Architect focused on the Distribution sector. Prior to Red Hat, Karl was with IBM for over twenty-five years and served as the Chief Architect for the Retail and Consumer Industry in addition to other assignments. He is also an IBM Master Inventor.
Rajeev joined IBM Global Markets as an Account Technical Leader focusing on distribution and communication sectors in the industry market. Rajeev has been a Client Facing Architect for the last 17 years serving various organizations like IBM Expert Services Lab and IBM Global Services.
チャンネル別に見る
自動化
テクノロジー、チームおよび環境に関する IT 自動化の最新情報
AI (人工知能)
お客様が AI ワークロードをどこでも自由に実行することを可能にするプラットフォームについてのアップデート
オープン・ハイブリッドクラウド
ハイブリッドクラウドで柔軟に未来を築く方法をご確認ください。
セキュリティ
環境やテクノロジー全体に及ぶリスクを軽減する方法に関する最新情報
エッジコンピューティング
エッジでの運用を単純化するプラットフォームのアップデート
インフラストラクチャ
世界有数のエンタープライズ向け Linux プラットフォームの最新情報
アプリケーション
アプリケーションの最も困難な課題に対する Red Hat ソリューションの詳細
オリジナル番組
エンタープライズ向けテクノロジーのメーカーやリーダーによるストーリー
製品
ツール
試用、購入、販売
コミュニケーション
Red Hat について
エンタープライズ・オープンソース・ソリューションのプロバイダーとして世界をリードする Red Hat は、Linux、クラウド、コンテナ、Kubernetes などのテクノロジーを提供しています。Red Hat は強化されたソリューションを提供し、コアデータセンターからネットワークエッジまで、企業が複数のプラットフォームおよび環境間で容易に運用できるようにしています。
言語を選択してください
Red Hat legal and privacy links
- Red Hat について
- 採用情報
- イベント
- 各国のオフィス
- Red Hat へのお問い合わせ
- Red Hat ブログ
- ダイバーシティ、エクイティ、およびインクルージョン
- Cool Stuff Store
- Red Hat Summit



